The SULTANATE OF OMAN, “Switzerland” of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) has outperformed other regional countries in terms of GDP growth and economic sustainability during the current fiscal year. It has diverse natural beauties and fascinating human history.
Comprehensive Development Plan
Once a middle-income economy heavily dependent on depleting oil resources, the Sultanate of Oman has been actively pursuing a comprehensive “development plan” focusing on “diversification of economy, resources and channels of production”, “massive industrialization” and “befitting privatization”, with the objective of reducing its reliance on the oil sector’s contribution to GDP and creating more employment opportunities for the rising number of young Omanis entering the workforce.
Blessings of Wise Leadership
The presence of wise leadership’s represented in His Majesty Sultan Qaboos Bin Said, who has a “far sighted” view on all issues, and the “immaculate capacity” to deal with potential developments and emerging trends. The Sultanate enjoys “political stability”, “social harmony” and “security” all over its lands.
Rigorous Reforms
It follows a “free market policy” and respects individual property rights. The natural resources available and the strategic “geographical location” of the Sultanate of Oman is considered one of the countries that provide a “suitable” and “encouraging climate” for “foreign investment”; this is particularly true after the “reformulation of laws” and regulations relating to this during 1994.
The government of Oman has been rigorously initiating various reforms to achieve the desired goals of diversification of economy. Being prominent regional expert of Oman/GCC, it is hoped that ongoing “structural reforms” will bring more “stability” and “sustainability” in its macro-economy wherein, tourism, service, construction, banking and human capital sector will achieve their targets in the days to come. It announced its diversification drive in 1995 which has now double its real income.
Resilient Banking System
Its banking system is resilient having regulatory and supervisory practices including risk-based supervision, implementation of Basel Accords and development of payment and settlement systems by the CBO. A pick-up in deposits mobilization eased liquidity pressure and banks were able to meet credit requirements without any difficulty during 2018. Its business and investment friendly policies have transformed monetary policy to foster growth with low inflation and financial stability.
It also indicated that banks in Oman continued to display resilience with adequate capital and low delinquency rates. There are 16 conventional commercial banks with a network of 449 branches, two government-owned specialized credit institutions with a network of 26 branches, and two full-fledged locally incorporated Islamic banks (the Islamic banks and conventional banks’ Islamic Windows together operated with 81 branches) at the end of 2018.
Smooth Sailing of Financial Markets
The financial markets generally functioned smoothly, albeit with varying performance across segments, and supported economic recovery. Notably, some upturn was witnessed in the volume of overnight inter-bank market, partly reflecting regulatory measures undertaken during the year. Overall, the banking and financial sector performed satisfactorily, supporting growth in the economy while persevering financial stability.
The CBO’s foreign assets increased by 8.1 percent during the year, reflecting higher oil prices, whereas the ratio of CBO’s net foreign assets to broad money remained more or less constant. While the broad money recorded robust growth, the money multiplier improved to 5.7 in 2018 from 5.0 in the previous year.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in Oman was worth 79.29 billion US dollars in 2018. The GDP value of Oman represents 0.13 percent of the world economy. GDP in Oman averaged 20.46 USD Billion from 1960 until 2018, reaching an all-time high of 81.08 USD Billion in 2014 and a record low of 0.04 USD Billion in 1960.
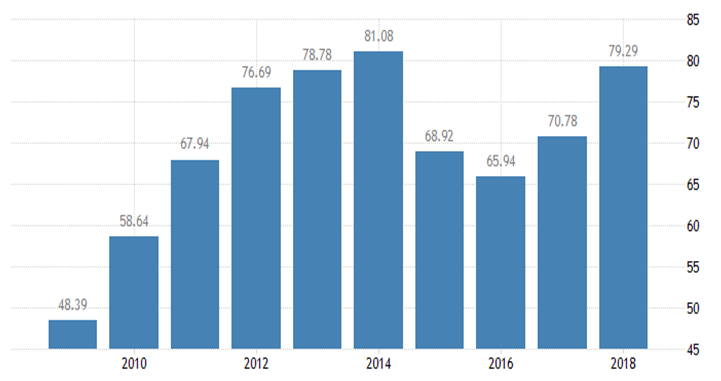
Oman GDP’s Future Prospective
According to Trading Economics global macro models (2018-2019) GDP in Oman is expected to be 79.50 USD Billion by the end of this quarter,. In the long-term, the Oman GDP is projected to trend around 87.50 USD Billion in 2020.
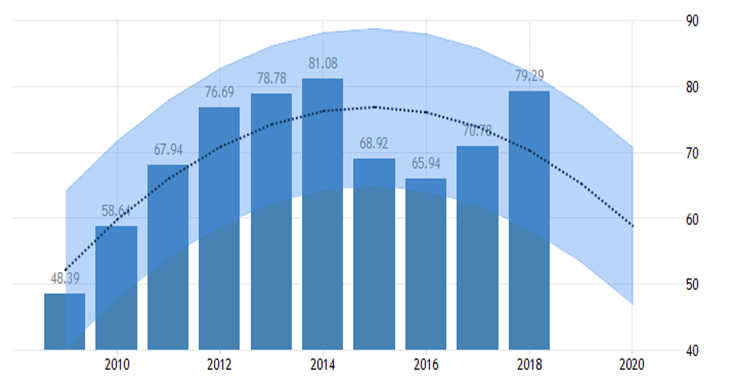
International Monetary Fund (IMF) 2019
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) in its World Economic Outlook report (2019) has now claimed that Oman will become the fastest growing economy in the GCC region next year. The sultanate’s real GDP is expected to grow by more than five per cent in 2019.
The IMF has revised up Oman’s 2019 growth forecast from 4.1 per cent projected in its April 2018 World Economic Outlook report.
Narrowed Fiscal Deficit
The fiscal deficit narrowed by nearly two-fifths in January-July compared to the same period a year earlier, thanks to higher revenue and a small cut in spending. However, the government remains highly reliant on volatile oil revenues.
Its macro-economy is expected to maintain steady momentum as fixed investment should benefit from low interest rates; OPEC+ oil production cuts. Turning to 2020, economic growth is projected to accelerate as continued low interest rates should sustain strong fixed investment growth.
National Drive of Diversification of Economy
Diversification leads to of economic stability and sustainability. Diversification further strengthens Omani national economy in case of any internal or external X-factor. Diversification further promotes elements of smarter economy, digitalization, automation and artificial intelligence. Oman’s has one of the largest tourist’s attraction in the GCC and MENA. It invested in the Park Inn in Muscat and the Golden Tulip in Nizwa. It is shortly opening the Park Inn in Duqm. A five star hotel in Salalah in a 50-50 private public partnership with Omran is near of its actual operationalization. Oman is also developing resorts on the coastline, and has four hotels under construction from four to five stars.
The government of Oman has been rigorously initiating various reforms to achieve the desired goals of diversification of economy. It is hoped that ongoing “structural reforms” will bring more stability and sustainability in its macro-economy wherein, tourism, service, construction, banking and human capital sector will achieve their targets in the days to come.
It announced its diversification drive in 1995 which has now double its real income. Oman’s Vision 2020 is a giant step towards economic liberalization, business & investment policies, easiness of doing business, rampant growth of renewables, and artificial intelligence which will paving the way for further and bolder reforms to be attempted under Vision 2040.
Oman Vision 2020
Vision 2020 was announced and implemented in 1995. It was design to steer the Sultanate toward a more sustainable and diversified economy by using oil revenues to boost investments in health, education, and social services, better train citizens, and raise living standards across the board. Oman’s Vision 2020 is a giant step towards “economic liberalization”, “business & investment policies”, “easiness of doing business”, “rampant growth of renewables”, and “artificial intelligence” which will paving the way for further and bolder reforms to be attempted and implemented under Vision 2040.
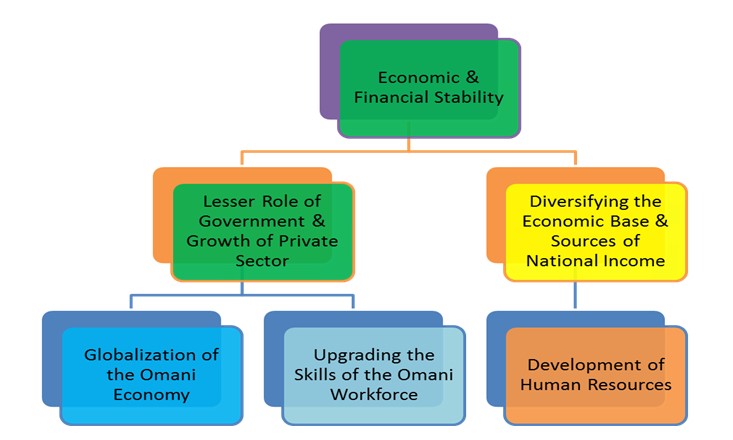
At the instruction of His Majesty Sultan Qaboos bin Said, Vision 2020, a plan for Oman’s economic future up to the year 2020 was set, outlining the country’s economic and social goals, which include: Economic and financial stability; Reshaping the role of government in the economy and broadening private sector participation; Diversifying the economic base and sources of national income; Globalization of the Omani economy; Upgrading the skills of the Omani workforce and developing human resources.
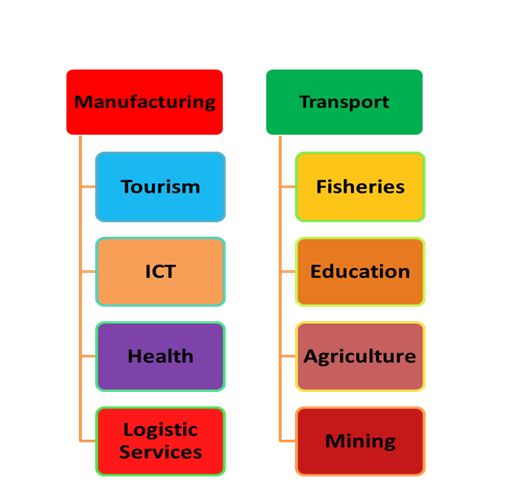
Oman: Pioneer of Strategic Visions
Oman is the “first country” in the GCC which announced and implemented Vision 2020 & 2040. The government is working hard to boost “Omanization”, throughout the economy, as much as possible. In addition to drastically boosting Omanization rates, Vision 2020 is also trying to increase women’s participation rate in the economy, encourage SMEs to bid on megaprojects, and boost the competitiveness of the private sector.
Omanization Policy
It also introduced rigorous Omanization policy in 2018 and subsequently, forced a six-month ban on employing foreigners in 10 sectors and 87 professions which included IT, media, engineering, accounting and finance, air traffic, insurance, marketing and sales, technicians, administration, and HR sectors.
Achievements of Vision 2020
According to its official figures (2019) more than 70 percent goals of Vision 2020 have yet been materialized. It was designed to double GDP per capita in real terms by 2020, the vision is almost on track: while the Sultanate boasted per capita GDP of USD6,261 in 1995 (USD10500 in late 2018), today it stands at USD15,700.
His Majesty Sultan Qaboos bin Saeed’ Strategic Vision
His Majesty Sultan Qaboos bin Saeed has strategic vision about his people and economy alike. He introduced Vision 2020 which enhanced the economic diversification. It has been implemented in the 9th five year development plan (2016-2020). The program also aims to draft a clear and accurate plan to increase external and domestic investments and follow up implementation of the economic diversification program. The industrial sector has for long been the foundation of Oman’s long-term diversification strategy as it is also capable of meeting the country’s social development needs and generating more employment opportunities.
Strategic Importance of Vision 2040
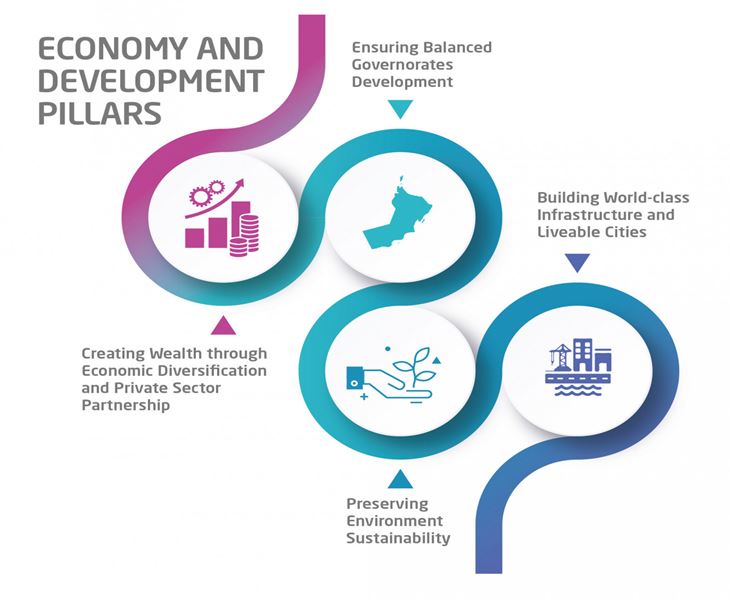
Vision 2040 & United Nation’s Sustainable Development Goals
Vision 2040 is aligned with the United Nation’s sustainable development goals. It focuses on various objectives. It has four important elements i.e. people, so that no one is left behind, knowledge based economy, protection and preservation of the environment and peace.The impetus behind Vision 2040 is to operate as the guiding document for the development of national implementation programs, including the next five-year plan between 2021 and 2025.
Vision 2040: A Coherent Development Framework
It is hoped that Vision 2040 will kindle a coherent development framework and galvanize the collective resources necessary to propel the Sultanate towards a sustainable, knowledge-based economy. Oman’s Vision 2040 provides good standards of living and employment.
Vision 2040 catalysts include facilitating the work environment, identifying private and government sectors, regulating work and productivity and making economic decisions quickly.”
Vision 2040: An Ambitious Strategy
Oman’s ambitious Vision 2040 strategy, first unveiled last year, seeks to catapult the Sultanate into the ranks of the world’s most ‘developed nations’, a top government official said here yesterday. It has a comprehensive “blueprint” and “roadmap” for achieving targets economic growth of around 5 per cent annually over the 2021-2040 timeframe.
Part of its Vision 2040 objectives is to nurture maritime hubs to leverage Oman’s strategic location at the crossroads of the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean, which eventually will pit them economically against the UAE. Moreover, Oman as a logistics hub is vital to China and other regional countries.
Transport & Logistics Infrastructure
Underpinning the transport and logistics infrastructure Oman has committed further development of ports of Duqm, Salalah, and Sohar. Duqm has now emerged as the Sultanate’s flagship venture. Envisioned as a significant engine for its diversification initiative, it has already seen substantial investment from the Chinese.
Human Capital & Knowledge-Based Economy
Developing people and creating a knowledge-based economy that focuses on individuals and their ideas, as well as maintaining peace are the cornerstones of Vision to 2040, and Oman is focusing on innovation, technology and protecting the environment as pillars for completing the vision and leading Oman to a future in tune with the United Nation’s goals.
Oman has decided to turn its attention towards young people and their needs in order to create a future suited to them. Vision 2040 is people centric and focuses on the young generation. It will definitely facilitate technological development and institutionalization, the fourth industrial revolution and empowering youth and women in society.
It has been designed to implement the plans and programs meant to achieve further prosperity of the Omani society and sustain economic growth, modernize the national economy and diversify its income sources and this will consequently lead to employment of more Omanis in the various economic sectors and promote the living standard in the various Omani governorates.
Development of Non-Oil Sector
A planned growth of non-oil sector has been pursued which is now paying its dividends. Being prominent regional expert of Oman & GCC it is hoped that these diversified but integrated structural reforms will increase investments, per capita income, overall GDP, role of non-oil sector in the national income to benefit all parts of the country.
Diversification Drive
Diversification leads to of economic stability and sustainability. Diversification further strengthens Omani national economy in case of any internal or external X-factor. Diversification further promotes elements of smarter economy, digitalization, automation and artificial intelligence. Oman’s has one of the largest tourist’s attraction in the GCC and MENA.
It invested in the Park Inn in Muscat and the Golden Tulip in Nizwa. It is shortly opening the Park Inn in Duqm. A five star hotel in Salalah in a 50-50 private public partnership with Omran is near of its actual operationalization. Oman is also developing resorts on the coastline, and have four hotels under construction from four to five stars.
Once a middle-income economy heavily dependent on depleting oil resources, the Sultanate of Oman has been actively pursuing a development plan focusing on diversification, industrialization and privatization, with the objective of reducing its reliance on the oil sector’s contribution to GDP, currently at 48.44 percent (USD 37.8 billion) and creating more employment opportunities for the rising number of young Omanis entering the workforce.
Oman’s Economic Growth Strategy
It underlines the development of simple industrial chains, particularly in basic manufacturing and allied activities as well as other industries that will enhance the Sultanate’s position and offer a competitive advantage in the region. The industrial sector has for long been the foundation of Oman’s long-term diversification strategy as it is also capable of meeting the country’s social development needs and generating more employment opportunities. Industrial sector has played a significant role in shaping the Sultanate’s economy in terms of accelerated growth, sustainable economic and social development and creating new jobs.
Other sectors such as tourism and gas based industries, banking and finance, healthcare and insurance, agriculture, retailing, aviation and recently the railways project, have also been key components of the government’s diversification strategy. The mineral industry in Oman is on a strong growth path.
Oman’s Mineral Resources
Oman’s mineral resources include chromite, zinc, limestone, gypsum and silicon among others. A large number of investors have been drawn into the sector as it is potentially expected to contribute significantly to the country’s GDP. Several industries have been developing around the mineral sector as part of the national development process, which as a result, has boosted the employment opportunities for a young Omani workforce as well as contributing to the nation’s GDP.
Sustainable Development & Increased Private Investment
One of the benchmarks for sustainable development and increased private investment is increased investment in infrastructure. Accordingly, the continuous development of Oman’s infrastructure and the availability of investment funds for such development projects is a determinant factor for the future growth of the economy. Government spending during the past few years on infrastructure projects such as roads, airports, seaports, hospitals and health centers are on the rise.
Fortunately, Oman’s government has taken a number of steps in terms of efficient economic planning and implementation of various social development initiatives that have contributed to the success of the Omani economy. Other factors that have contributed to Oman’s success include the significant rise of foreign investment in many sectors as a result of competitively low tax rates in the region. The development of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) together with ICV strategy lays a solid foundation for self-reliant industry and modernization of the economy. Despite the various challenges within the region and in the country, Oman’s economy is set on the right path of sustainable growth, development, diversification and progress.
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) is one the important part of Oman’s diversification policy. It has focused on the growth and development of small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to compete in the international arena, beyond the domestic markets.
Development of Human Capital
The Omani government has a strong desire to have Omani nationals play a leading role in all areas of trading and professional employment in the Sultanate. As a result, education and training are prioritized and has been a cornerstone of each of the Sultanate’s five-year development plans. The Ministry of Education’s commitment to a sector that while maintaining traditional values is modern and advanced, is reflected in its range of educational programs, including the basic education system, designed to meet the demands of modern science and culture in the information age.
Tourism
It is one of the leading non-oil sectors in the macro-economy of Oman. It is being further developed as an important and sustainable socio-economic sector of the Sultanate of Oman in a manner that reflects the Sultanate’s history, cultural and natural heritage and spirit of traditional hospitality. Tourism will facilitate economic diversification, the preservation of cultural integrity and the protection of the environment of the Sultanate. According to the latest figures (2018-2019), tourism contributes approximately 2.4 percent to Oman’s GDP and is expected to increase to 3 percent by 2020. There is a significant increase in investment in the tourism sector creating considerable jobs.
Taxation
To attract more and more ratios of Foreign Direct Investments (FDIs), Oman introduced a new tax law that consolidates a number of ministerial decisions, interpretations and practices arising from the previous 28-year old law, along with the introduction of certain new tax regulations in 2019. It has now eliminated the discrimination in tax rates between the branches of foreign companies and Omani companies/establishments and the introduction of a unified rate of 12 percent applicable to all business concerns.
Further, under the U.S. Free Trade Agreement, American companies can register a limited liability company with 100 percent foreign ownership without the involvement of a local partner. The reduction in tax rates, the amendment to the definition of “permanent establishment,” which is now in line with the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) and the free trade agreements entered into by Oman, has encouraged and increased foreign investment in Oman. Another major change introduced by the new tax law is a shift from a territorial system of tax to a global system of tax, whereby revenue earned outside Oman is also taxed and which, consequently, increases the government’s revenue from tax.
Omanis in the private sector represents about 15 per cent of the total workforce, attributing this to the weak role of the private sector in the economy.
Oman-Pakistan Bilateral Relations
THE SULTANATE OF OMAN and Pakistan are “strategic partners and neighbors”. The arch of political, parliamentary and military exchanges has been getting momentum since 2017. Oman and Pakistan are natural partners due to geographical proximity and the leadership, Government and the people of Pakistan hold His Majesty Sultan Qaboos bin Said Al-Said and the brotherly people of Oman in high esteem.
Relations between Oman and Pakistan are excellent close, warm, brotherly, cordial and deep. Both countries are members of UN, OIC and NAM. There are over 250,000 Pakistani immigrants resident in Oman. 30 percent of Omanis are of Balochi origin from Pakistan’s Balochistan province, having settled in Oman over a hundred years ago.
The Sultanate of Oman: Pakistan’s Closest Arab Neighbor
The Sultanate of Oman is Pakistan’s closest Arab neighbor too. Oman places heavy emphasis on the values of tolerance, peace and co-existence with other faiths. Oman relationship with Pakistan has been established on a solid foundation originating before contemporary Pakistan. An introspection of the two countries would highlight strong reasons for further bilateral cooperation in the areas of defense, trade, tourism, human resources, oil gas, ports, industry, CPEC, Infrastructure and foreign policy.
Enhanced Cooperation
Most recently, both countries have agreed to enhance cooperation in the fields of trade and economy given the geographical closeness of Pakistan and Oman. Oman considers Pakistan a “gateway” for Oman access to the Central Asian States. Being prominent regional expert to Oman/GCC it is strongly recommended that bilateral cooperation can be further strengthened and taken to the new heights by improving economic relations.
Creation of Pak-Oman Friendship Group
On its part, Pakistan attaches great importance to its relations with Oman and is keen to further enhance these brotherly relations in all spheres. It is hoped that the creation of Pak-Oman Friendship group in the Consultative Assembly (Majlis A’ Shura) of Oman would further connect the two countries. Moreover, regular high-level interactions through established mechanisms of Bilateral Political Consultations and Joint Commission would promote and expand bilateral ties in diverse fields.
Bilateral Trade However, the current level of bilateral trade is not match with excellent political ties and highlights the need to diversify bilateral trade by taking advantage of geographical proximity, the investment friendly policies of Pakistan, and Pakistan’s potential of exporting food items, construction materials, leather and surgical goods to Oman. Pakistani community has been making valuable contribution to the development of Oman which needs to be increased in employment of Pakistani workers in banking, health, education, petroleum and food sectors.
Healthy Signs
The bilateral trade relations between Pakistan and Oman are on the rise. According to Pakistan’s official figures (February 2018), Pakistan exported goods to Oman worth $ 142.3 million which is 67 percent higher than $ 85.2 million worth of exports in 2017. The volume of goods imported from Oman was recorded at $ 234.1 million in 2018 higher by 21.7 percent as compared to $ 192.4 million worth of imports in 2017.
The trade balance, which stood at $ 91.8 million, has bettered by 14.9 percent in favor of Pakistan as compared to $ 107.19 million in FY17, yet it needs attention of the govt. authorities as to how Pakistan’s volume of export to Oman could be enhanced. Nonetheless, trade volume has been increasing but there is also a need to enhance the overall trade volume by making joint cooperation in different fields of economy.
For the further strengthening of bilateral trade and business activities between both the countries, a joint business council of Chambers of Commerce of Pakistan and Oman is going to set up in Oman. Oman can add to further economic cooperation with Pakistan by virtue of investments as vast prospects of investment lies in industry, livestock, energy, agriculture, information technology. Moreover, Pakistan can tremendously benefit from Oman’s technological advancement in the oil & gas sector.
Socio-Economic Integration & Regional Connectivity
Further socio-economic integration and regional connectivity of both the countries are also linked with each other. It forms a strong impetus for fostering comprehensive bilateral cooperation between Pakistan and Oman in light of their mutually shared interests. Oman’s special spot in the GCC/ MENA in terms of its foreign policy maneuvering, ethnic composition, and proximity with Pakistan are factors that will facilitate the strengthening of relations between Pakistan and Oman. It will also provide Pakistan with a strategic partner in the Gulf.
Pak-Oman Investment Company
Pak-Oman Investment Company is the prime example of increasing financial cooperation between the two countries which has been established with $100 million during the visit of Sultan Qaboos. It has a strong focus on infrastructure development and SME financing. It is one of the seven joint venture (JV) development financial institutions which the Government of Pakistan has established with its strategic partners including China, Saudi Arabia, and Brunei, to name a few. Pak-Oman is one of the most profitable such JV for the last many years. The assets of the company have now increased up to $600 million. Both Pakistan and Oman offer immense potential for economic growth, as well as social development and can leverage on each other’s expertise in various sectors.
Pak Oman Microfinance Bank
Pak Oman Microfinance Bank Limited has also been established in order to enhance trade between Oman and Pakistan. Both the countries have also agreed that bilateral accords on defence cooperation, business sectors, labour and manpower which are in their final stages needed to be brought to fruition.
Bilateral Energy Cooperation
It is pertinent to mention that key industries of Oman are crude oil production and refining, natural and liquefied natural gas (LNG) production, construction, cement, copper, steel, chemicals and optic fiber. Oman’s major export commodities are petroleum, organic chemicals, metals and fertilizers to partners China, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar and India. Its main imports are machinery and transport equipment, manufactured goods, aircraft, food, iron and steel from partners UAE, India, China, Saudi Arabia, Brazil and US. Pakistan’s exports to Oman mainly include cereals and meat. Major imports from Oman are POL products, iron and steel, plastics and organic chemicals.
Bilateral Ties in Petroleum Sector
Pakistan and Oman desires to boost bilateral ties in petroleum sector. The delegation from Oman showed the desire of expanding ties with Pakistan. The delegation displayed a keen interest in getting engaged with the Petroleum Sector of Pakistan including the signing of a MoU with the Pakistan LNG Limited, surging the gasoline volumes, LPG and petroleum products. The government of Pakistan assured the visiting delegation that all measures would be taken for facilitating the OTI’s activities in the Pakistani market.
Pakistan is constantly updating its infrastructure to increase LNG imports from Oman to alleviate its energy shortage. The value of Pakistan’s exports to Oman stands at approximately USD $118 million, well below to its potential. The poultry industry, for instance, is a niche that Pakistan could foster with Oman. Presently, Oman imports around 57.5 percent of its poultry, while Pakistan produces a poultry surplus. Likewise, Oman could export energy resources to Pakistan. Thus, Oman could be a potential source of uncharted economic possibilities, representative of other unexplored areas of cooperation in Pakistan-Middle East economic relations.
Maritime Cooperation
Pakistan shares a maritime boundary with Oman. Based on the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) coastal countries are allowed economic control of the waters and seabed up to 200 nautical miles from their shores. 24 In March 2015 Pakistan became the first country in the North Indian Ocean region to be granted an extension by 350 nautical miles of Continental shelf by the United Nations.25 This added 50,000 Sq Km of seabed territory to the already existing 240,000 sq Km of Pakistan’s exclusive economic zone26. Hence, this brought Pakistan physically closer to Oman.
Military Cooperation
Most recently, Oman’s Chief of Staff of Sultan’s Armed Forces Lt General Ahmed Bin Harith Al Nabhani visited Pakistan and met with various high officials including Prime Minister Imran Khan who reiterated the government’s resolve to further deepen bilateral cooperation between Pakistan and Oman in diverse fields. The Prime Minister highlighted the close, cordial relations between the two brotherly countries. Matters related to enhancement of trade and transportation links were also thoroughly discussed.
Lt General Ahmed Bin Harith noted the strong Oman-Pakistan bilateral relations and expressed satisfaction over the existing level of defence cooperation, including frequent exchange of visits, training exchange programs and joint exercises.
Pakistan army chief, General Qamar Javed Bajwa also met with the Chief of Staff of Sultan’s Armed Forces of Oman, Lt. Gen. Ahmed Bin Harith Al-Nabhani, at the General Head Quarters (GHQ). During the meeting matters of mutual interest and regional situation were discussed. “The visiting General lauded Pakistan Army’s achievements in the fight against terrorism and continued efforts for regional peace and stability.
Concluding Remarks
The Sultanate of Oman under the “strategic leadership” of HIS MAJESTY SULTAN QABOOS BIN SAID has already achieved “economic miracles” in the age of weak global economic prospects. Massive diversification of economy, resources and channels of production has already transformed it into a “hot attraction” for the foreign companies and investors alike to make huge investments in the country. Future economic prosperity, high ratios of GDPs, GNPs, social development, high literacy rate, provision of best medical facilities and housing are heavily dependent on its ongoing structural reforms under the umbrella of “Vision 2020 & 2040. Both are “game and fate changers”.
Peace, one of the integral parts of Vision 2040 is a “cashable commodity” which has “multiplier effects” in Oman’s persuasion to achieve “unshakeable” “economic stability” and “sustainability”. Peace has “direct correlation” with political stability and Sultanate of Oman is undoubtedly enjoys “political steadiness” despite widespread virus of so-called “Arab Spring” in the region. Oman’s future economic prosperity and political stability is deeply dependent on massive diversification, knowledge based economy, influx of FDIs, further development of tourism, SME, further empowerment of women, Omanization, services, banking & financial sector, aviation, sea economic routes, and above all further strengthening of non-oil sector in the days to come.
Frequent meaningful exchange of Chambers of Commerce, businessmen and investors is the need of the hour. Social sector of both the countries offer a befitting proposition which may lead to immense socio-economic prosperity of the both the countries in the days to come. Rapidly changing geo-political and geo-strategic emerging trends require further better political understanding and consultative mechanism between the two countries and HIS MAJESTY SULTAN QABOOS BIN SAID AL-SAID is “economic guru” and “political magician”.
His Majesty Sultan Qaboos Bin Said Al-Said has introduced a “holistic approach” to achieve desired goals of socio-economic development. Human capital has been one the main priorities of his esteemed policies of diversification of national economy embodied with Visions of 2020 & 2040.
“Development is not a goal in itself. Rather, it exists for building man, who is its means and maker. Therefore, development must not stop at the achievement of material wealth and a diversified economy. It must go beyond that to contribute to the formation of the citizen who is capable of taking part in the process of progress and comprehensive development. Such goals can be achieved through the improvement of the citizen’s technical and professional ability, the stimulation of their creative and scientific capabilities, and the improvement of their diverse skills. All this must be directed towards serving the country and achieving the happiness of all citizens.”
Oman’s determination to achieve the goals and targets set out in the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development constitutes a natural extension of the values and principles of sustainability, equality, justice, peace, engagement, and “leaving no one behind” that have been deeply rooted in Omani society since its inception. Oman has been on the right path to achieve all these goals even before time.
Oman has contributed to peace, safety, and stability within its borders and in the region, during the transition from the 1970s to the 21st century. Its economic and social achievements have boosted the living standards of Omani citizens. The establishment of the basic law of Oman and its amendments has ensured the rule of law. Now it has allowed deep cooperation between executive and legislative institutions within the framework of equality, independence of the judiciary, and facilitation of justice for citizens.
The Sultanate has won recognition in a number of competitiveness indicators released by international institutions. For example, it ranks first in freedom from terrorism, reliability of police services, independence of the judiciary, road quality, efficiency of port services, and open data. All these reflect the efforts of the government in various economic, social, service, and other sectors.
To fulfill the requirements of Oman Vision 2040, and launch the Omani economy into a new stage and attract investments, the Sultanate is making extensive efforts to promote its favourable investment climate and facilities, including the Special Economic Zone at Duqm and free zones elsewhere.
Oman has been followed its diversification drive on the basis of “Malaysian Model” since 1995. It was launched to develop non-oil sector. It has successfully created favourable conditions for private sectors in the country due to which its service, tourism, banking and finance, aviation, construction and last but not the least infrastructure has been revolutionized.
Being prominent regional expert of Oman & GCC it is strongly recommended that a ferry service between Karachi, Gawadar and Muscat “this initiative may start a new chapter of friendship between two brotherly countries and the service will provide an affordable alternative source of movement for a large number of people who move on these routes on regular basis. It is hoped that once implemented this development would have great geostrategic potential. It would link not only Oman but the entire Gulf region to the China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC). If the ferry service were to include vehicular carriage, it would be possible to drive from Karachi to Dubai via Muscat. In this regard, “Oman may seek help from “Singaporean Model” for the further development of its seas routs and blue economy in the days to come.
It could boost the tourism sector of both Pakistan and the Middle East. Trucks from Oman could be loaded with goods and transported using the ferry service to Pakistan from where it could be linked to CPEC. It would also enhance the unique position of Pakistan in the vicinity. In effect this will deepen Pakistan’s foreign relations with Oman. As such this ferry service should be taken on a serious note as it could prove to be a major game changer bridging Pakistan and Oman.
The success of its strategic visions 2020 & 2040 is dependent on constant structural reforms to further strengthen the national drive of diversification. In this regards, Oman should seek help from China, its private companies, FDIs and creation of various free economic zone to achieve the desired targets of socio-economic development. Its tactful regional maneuvering has saved it from any regional political conflict. Its neutral posturing has been savior of its territorial integrity and people’s sovereignty. Its strategic thinking beyond GCC/MENA has now opened new window of opportunity which may be used to eliminate regional disharmony and promote regional peace in the days to come.
Ours is the age of commercial diplomacy which also gears-up bilateral relations. In the modern arena of bilateral relations trade commerce, joint ventures, inflows of foreign direct investments, free economic zones/corridors and above all strong political commitment plays an important role in achieving sustained bilateral relations. Oman and Pakistan have great potential to excel especially sharing various untapped opportunities between them in terms of defence production, procurement, training, agro-based food security, climate change, vegetarian & fruit cooperation (exports of mangos & oranges), verbal medicines, flora, infrastructural development and manpower etc. Further strengthening of bilateral relations should be trade oriented, diversity of export mix, energy cooperation (oil, gas, and renewables), science & technology, education, tourism, and service sector in the days to come.




