Turkmenistan maintains its neutral status since its independence. Its neutrality is basis of its foreign policy. In the 21st century concept of neutrality is based on national interests. It shapes foreign policy, it formulates national security policy, cares about sovereignty and national dignity and preserves political stability and promotes economic self-reliance.
Diversified Dividends
Turkmenistan’s neutral status plays a very important part in its onward march in the fields of macro-economy, social development, massive industrialization, diversification of economy, green energies and above all a stable political system. It has been pro-development, human and institutionalizes spirits of diplomacy, conflict resolution and above all dialogue for achieving desirable goals of regional peace and harmony in the region. It also promotes energy security in the region and increases regional connectivity. It was and is guarantor of political stability and economic prosperity, civil consent and social concord in the country.
UN General Assembly Resolution (2017)
Last year, the UN General Assembly (UNGA) adopted a resolution and declared 12 December as the International Day of Neutrality. The said resolution was introduced by Turkmenistan. It was recognized by the UNGA as a permanently neutral state since 12 December 1995.
The Turkmenistan model of neutrality comes from the fact that contemporary international law has the right to peace and a permanently neutral state must adhere to its status, not only in war but also in peacetime. As a new phenomenon in international legal practice Turkmenistan neutrality suggested the international community fundamentally change the global development paradigm, becoming the basis of a new concept of cooperation and achievement of world peace.
Turkmenistan’s successful model of neutrality is now of the greatest interest to political and research centres around the world. Respect for sovereignty and territorial integrity, peacefulness, non-interference in the other affairs of other states, and close international liaison for achieving greater peace, harmony and sustained development are the salient features of its neutrality status which is based on peace and non-violence.
Constitution and Permanent Neutrality Status
The UNGA resolution on the International Day of Neutrality (document A/71/L.56) notes the link between the preservation of peace and the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. It is based on peace, justice and broadening economic opportunities. Its present law determines political, economic and humanitarian grounds for the permanent neutrality of Turkmenistan. The status of Turkmenistan’s permanent neutrality is based on strict and absolute adherence to the letter and spirit of the Constitution, UN Charter and international obligations. It has gained credibility and trust among other states and will create favourable external conditions for internal stability and sustainable development.
| Articles | Details |
| Article I Permanent Neutrality | The permanent neutrality of Turkmenistan is the basis of its foreign and domestic policy aimed at strengthening the stability and consent in society, developing the friendly and mutually beneficial relations with the states of the region and the whole world. |
| Article II Acceptance of the permanent neutrality | The acceptance of the permanent neutrality status by Turkmenistan does not affect the obligations’ performance of Turkmenistan, arising from the UN Statute. Turkmenistan will promote the achievement of the UN objectives in every possible way. Turkmenistan recognises the priority of the United Nations Organisation and its decisions. |
| Article III Persuasion of Peaceful Foreign Policy | Turkmenistan pursues the peaceful foreign policy, makes its relations with other states on the principles of equality of rights, mutual respect and non-interference to internal affairs of other states. |
| Article IV Stay Away from War Blocs & Alliances | Turkmenistan does not participate in war blocs and alliances, interstate associations with tough obligations or providing the collective responsibilities of the parties. The activity of foreign policy of Turkmenistan does not restrict, and doesn’t infringe the other states’ interests, and does not threaten their safety. |
| Article V No War, No Conflict | Turkmenistan commits itself not to start the war and war conflicts, not to participate in them (except of the exercise of right to self-defence), not to take political, diplomatic or other steps that could bring to war or war conflict. In case of armed aggression against Turkmenistan it is entitled to appeal for the help to another states or the United Nations Organisation. |
| Article VI Nuclear Free Country | Turkmenistan will not have, produce and distribute nuclear, chemical, bacteriological and other weapons of mass defeat, allocate the military bases of foreign states. |
| Article VII Economic Cooperation on Equal Basis | Turkmenistan develops the international economic cooperation on the basis of equality of rights, mutual benefit and accounting for the interests of the parties involved into this process, considering such cooperation as an important means of strengthening trust between countries and regions, and maintaining peace and stability. |
| Article VIII Open for Financial & Economic Assistance | Turkmenistan provides its financial and economic space open, cooperates with all states, international economic and financial organisations, promotes the world community efforts when solving the economic problems. Turkmenistan considers the economic pressure of one state on another one unacceptable as a means of gaining the political objectives, and does not participate in economic blockade announced by them. |
| Article IX Custodian of Democratic Rights | The highest value of the society and state in Turkmenistan is a person. Turkmenistan recognises and respects the basic democratic rights and liberties of a person and a national accepted by the world community and fixed in the international law standards, creates political, economic, legal and other guarantees of their efforts’ exercise. In Turkmenistan the equality of rights of all nations and nationalities, the religious liberty are provided. |
| Article X Foreign Relations on the basis of Mutual Respect | Turkmenistan makes its relations with other states on the basis of respect of their culture, traditions and customs, and considers the humanitarian contacts as the most important means of making the people close, deepening the mutual understanding between them, developing relations of friendship and co-operation. Turkmenistan promotes the exchange of spiritual values between nations and nationalities, mutual enrichment and imbedding of cultures. |
| Article XI Joining of International Legal System | Turkmenistan joins the basic international legal acts providing the rights of refugees, displaced persons and compelled migrants, maintains the efforts of the states and international public relating to rendering help to countries suffered from wars, conflicts, natural calamity, catastrophes, epidemics and their consequences. Turkmenistan collaborates actively with world and regional humanitarian organisations |
| Article XII Guarantor of Domestic & Foreign Policies | Turkmenistan guarantees the steady and strict conformity of the course of its domestic and foreign policy with the permanent neutrality status and international obligations taken upon it in connection with that. |
New Concept of Cooperation & World Peace
The above table clearly shows that UNGA Special Resolution on 12 December 1995 entitled ‘On the Permanent Neutrality of Turkmenistan’ became a recognition of the peaceful foreign policy of Turkmenistan which contributions peace and harmony in international relations, It ensures universal security and steady progress. Its neutrality has become the basis of a new concept of cooperation and achieving world peace. Recognition of Turkmenistan’s permanent neutrality has been a novelty in the history of world politics. In 1995, 185 UN member states voted unanimously for its adoption in the UN General Assembly. Today, Turkmenistan is the only state that has been recognised as having a status of permanent neutrality by the UN, and this major international organisation has become the guarantor of the country’s status.
Neutrality and Foreign Policy
The open and peaceful character of Turkmen neutrality focuses on joint prospecting and the solution of problems at both regional and global levels has been positively received around the world. Turkmenistan’s neutrality status maintains unwavering to its international legal status, and reaffirms that neutrality, peace and good neighbourly relations constitute the basic foundation of its foreign policy. It stands for the preservation of peace in the world and development of friendly relations among all nations. It promotes solidarity on the strength of humanistic principles. It has played an important role in establishing broad cooperation with the countries of the world in the political, economic, cultural, scientific-educational and other spheres.
Significance of Neutrality & Emerging World
The world has become more polarized and dangerous because of emerging political, social and economic negative trends. Uncertainty is everywhere. Political tussle has deformed issues of larger cooperation for achieving stability in the world. Economic and trade wars have worsened the prospects of a sustained path of economic prosperity. Economic nationalism has become a bitter reality where economic freedom, fair competition and above all globalization are being dismantled. Social divide has put the world on the default line where faiths and civilizations are struggling. US-EU tariff stand-off has weakened bright prospects of the global economy. US-China trade tariff has marginalized “East-West” economic cooperation. Moreover, the refugee crisis has diminished the spirits of humanity and harmony too. Regional cooperation and global peace is at stake because of power politics. Neutrality Status may play very important in resolving emerging conflicts in the world. The neutrality status of Turkmenistan has encouraged a number of regional and global processes in energy security, transportation and transit, communications and other areas.
Turkmenistan’s Voluntarily Acceptance
Turkmenistan voluntarily accepted the status of permanent neutrality as a result of a conviction that such status is vital to the country’s independence and sovereign development. It has enabled Turkmenistan to select the most productive areas of cooperation, forming a modern security system and mechanisms for peaceful, political solutions to regional and international conflicts, all aiding risk and threat prevention.
Integrated Benefits
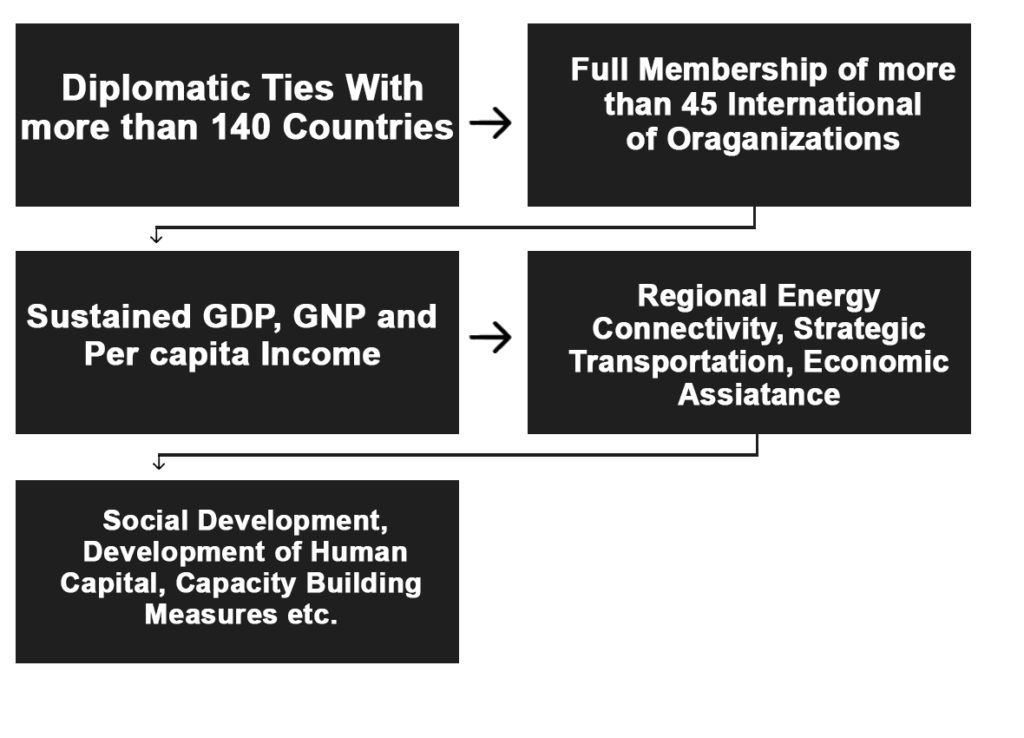
By virtue of neutrality status Turkmenistan has reached many significant milestones, it has established diplomatic relations with 140 countries and has become a full member of 44 international, multilateral and regional organisations, including the UN and its specialised agencies, the Organisation for Security and Co-operation in Europe, the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, and others. The status of neutrality also contributes to Turkmenistan’s economic development, and the transformation of the country into one of the most active political players in the region, strengthening security and stability in Central Asia and the Caspian Basin.
Meaningful Energy Cooperation & Connectivity
Turkmenistan continues to expand international cooperation in energy, its initiative regarding energy security involves creating an international legal mechanism governing the reliable and stable transit of energy resources. Supported by the international community, this initiative has been specifically promoted by Turkmenistan in all relevant international arenas since its initiation in 2007. Turkmenistan’s Chairmanship 2017 of Energy Charter Treaty and holding of Strategic Transportation Conference 2016 shows its strong commitment towards achieving greater regional cooperation. Turkmenistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan-India Gas Pipeline is a prime example of its neutrality status which always cooperates with other regional countries to achieve desired goals of socio-economic integration and regional connectivity.
Dignified Participation
Turkmenistan has been thrice elected as Vice-Chair of the UN General Assembly at the 62nd, 64th and 68th sessions, and as a member of the UN General Committee has been closely involved in the development and approval of the agenda of those sessions.
In 2012 for the first time Turkmenistan was elected to one of the main UN Councils, the Economic and Social Council, for the period 2013-15. This was undoubtedly in recognition of the country’s contribution to seeking out and implementing solutions to economic and social development global issues.
Turkmenistan’s election to UNESCO’s Executive Committee for the period of 2013-17 was the result of widespread social reforms undertaken by the country, as well as Turkmenistan’s state policy of broad international cooperation, focusing on partnerships in humanitarian and cultural arenas.
Turkmenistan’s Conflict Resolution
Turkmenistan firmly supports political and diplomatic methods of settling internal and interstate conflicts. As alternatives to the military approach, political and diplomatic methods can serve as the foundation for durable solutions and can offer the keys to sustainable peace and stability. Accordingly, Turkmenistan’s leader Gurbanguly Berdimuhamedov initiated the adoption of the UN Declaration prioritising political and diplomatic means in solving international issues, which offers a kind of universal guide to resolving international problems with the appropriate tools.
Foreign Policy Resource & Political Diplomatic Tool
The neutrality status of Turkmenistan has become a foreign policy resource and a political diplomatic tool to achieve peace, security and sustainable development. Mongolia showed great interest in successful model of Turkmenistan’s Neutrality Status. Mongolian President Mongolyin Tsakhiagiin Elbegdorj declared the country to be a permanently neutral state at the UN General Assembly. Besides Switzerland and Turkmenistan, which are permanently neutral states, some other countries such as Austria, Finland and Sweden also stick to neutral foreign policies.
| Countries | Real Motives |
| Austria | It adopted neutrality to stop foreign occupation and end further division of the country. |
| Finland | It was political survival tactic to maneuver between West and Soviets. |
| Switzerland | It implied non-participation in alliances in peace times. |
| Turkmenistan | Unique model of permanent neutrality which is the basis of internationalism and globalization. It values humanity and encourages human development. It was and is desire of its people. No external threat or international compulsion for adopting status of neutrality. It was a wise decision of its national leader. |
Neutrality & Turkmenistan Success History
Despite the scarce number of neutral states in the world nowadays, they are an important part of the current complex international framework. Turkmenistan’s history of success and achievement in domestic and foreign policy is a clear indication that the country’s neutrality is not only a strong pillar of its independence and sovereign foreign policy, but also a platform for the promotion of initiatives and proposals aimed at promoting the development of global political, economic, cultural and humanitarian cooperation.
Neutrality: Anti-Conflicts & Wars
Its neutral position has helped Turkmenistan avoid various conflicts and wars. At the same time, Ashgabat has taken an active part in mediating regional conflicts such as the ones between Tajikistan and Afghanistan. In 2007, the UN Regional Centre for Preventive Diplomacy for Central Asia was set up in Ashgabat, which consolidates the country’s neutral position on the world stage.
Main Doctrine
Neutrality is its main doctrine, it strives summons to protect peace on the planet, develop friendly relations between the people declaring humanitarian principles and promotes solidarity. Turkmenistan demonstrates true adherence to its international legal status practically proving that the neutrality, peace-loving and good neighbourhood are the basis of its foreign policy.
Neutrality & Socio-Economic Reforms
After two decades, the neutrality status has become not only the foundation for successful implementation of large-scale transformation state programs and social and economic reforms but also an important factor of peace and stability in the Central Asia, expansion of versatile cooperation with all interested countries of the world and largest international and regional organizations.
Neutrality & Turkmenistan’s Economic Achievements
Turkmenistan’s economic achievements could not have been successful without its neutral stance. Since its independence, its politics and economy remained stable. In 2014, its GDP growth stood at 10.3 percent. Turkmenistan turned from a supplier of raw materials into a rapidly developing modern industrial country. Under the people-oriented principle, the Turkmen government has been making efforts to improve people’s lives. The country is the only one in the world that provides the public with salt, water, natural gas and electricity for free.
| Years | GDP % |
| 2006 | 11 |
| 2007 | 11.1 |
| 2008 | 14.8 |
| 2009 | 6.1 |
| 2010 | 9.2 |
| 2011 | 14.7 |
| 2012 | 11.1 |
| 2013 | 10.2 |
| 2014 | 10.3 |
| 2015 | 6.5 |
| 2016 | 5.4 |
| 2017 | 5.4 |
The above table clearly shows that Turkmenistan’s macro-economy has been achieving high rates of GDPs since its inception. Some economic and political events had a negative impact on Turkmenistan’s economic growth, which had slowed due to the geopolitical situation, a drop in oil and gas prices, insufficient economic development in that are trade and economic partners of Turkmenistan, fluctuation of foreign currency exchange rates, instability of securities on stock markets and other reasons.
Council of Elders of Turkmenistan (2018)
According to Council of Elders of Turkmenistan (2018), Turkmenistan is expecting 6.2-8.2 percent annual GDP growth during 2018-2024. New national socio-economic development program has been announced that sets the task of mobilizing all resources and opportunities for the stable growth of the national economy and rapid transition to market relations, particularly fast development of non-governmental segments of the economy. Establishment of joint ventures and joint stock companies, development of stock exchanges and securities markets will also be stipulated. The program states that industry will account for 33 percent of GDP, construction 14 percent and agriculture 10.9 percent during 2018-2024. Transport and communication branches will achieve 9.1 percent, trade 12 percent and services 21 percent.
The GDP in Turkmenistan expanded 6.20 percent in the first quarter of 2018 over the same quarter of the previous year. GDP Annual Growth Rate in Turkmenistan averaged 6.86 percent from 1994 until 2018, reaching an all-time high of 16.50 percent in the fourth quarter of 1999 and a record low of -17.30 percent in the fourth quarter of 1994.
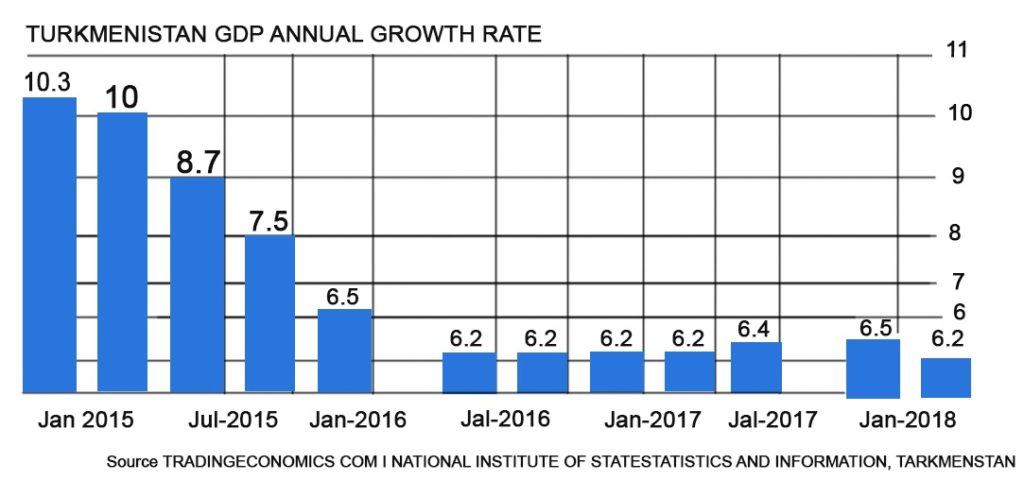
Turkmenistan Fastest Growing Economy
Turkmenistan has been one of the fastest growing economies in recent years. The most important sector of the economy is oil and natural gas extraction, which accounts for more than 60 percent of GDP. Although agriculture accounts for only 10 percent of GDP, it employs 50 percent of the labour force. Turkmenistan is the world’s largest producer of cotton per capita. While the government has recently enacted much needed reforms in agriculture and banking, reduced subsidies for fuel and is promoting tourism. Furthermore, bureaucracy and corruption still hamper foreign direct investments.
Expected Economic Prospects
Years | GDP % |
| 2015 | 6.5 |
| 2016 | 6.2 |
| 2017 | 6.5 |
| 2018 | 6.5 |
| 2019 | 6.7 |
Source: Asian Development Bank (2018)
GDP per Capita
| Selected Economic Indicators | Real Motives |
| GDP per capita/current prices | 7,144.1 (IMF World Economic Outlook 2016) |
| GDP per capita-PPP | 18,414.8 (IMF World Economic Outlook 2017) |
GDP Composition by Sector
| Selected Economic Sectors | GDP % |
| Agriculture | 13.2 |
| Industry | 47.7 |
| Services | 39.2 |
The above diagram verifies that Turkmenistan is an economic leader in the region which is well connected and blessed with unlimited natural resources in terms of oil and gas. It is also a connecting hub to Central Asia and South Caucasus.
Concluding Remarks
Turkmenistan’s neutrality status is one of the balancing acts in terms of its marvelous socio-economic development. It was not a compulsion but a national consensus of leaders of Turkmenistan and its common people. It was not out of fear but collective wisdom of the nation, based on its rich traditions, civilization, and customs. It secured Turkmenistan’s strategic assets. It protected civil liberties and basic human rights.
It guaranteed basic necessities of life. It was its first comprehensive policy to be useful part of regional as well as international peace and harmony. Now it has become an effective tool to achieve desired goals of socio-economic integration, greater energy connectivity and the last but not the least, qualitative life. Moreover, it stands for diplomacy, dialogue and development. It is an effective tool for conflict resolution which can be used for achieving a stable world and sustained economic growth in the world.
Neutrality is not just a legal status of Turkmenistan ratified at the international level that focuses only on the national interests. In fact, this is the unique embodiment of the world’s culture and development in the name of the universal interests. Turkmenistan’s activity at the international arena, in particular under the aegis of the United Nations Organisation, vividly testifies to the constructive character of the policy of positive neutrality.
Turkmenistan is the champion of diplomacy which it serves to prevent and settle conflicts, ensure security and sustainable development. Turkmenistan’s efforts in the political and economic revival of neighbouring Afghanistan, including in the framework of the systematic implementation of a number of important international projects and initiatives, stand as a bright evidence of the task-oriented phenomenon of the policy of positive neutrality.
Ashgabat hosted the 7th Regional Economic Cooperation Conference on Afghanistan (RECCA-VII) to promote the further consolidation of the joint efforts to develop the mutually agreeable approaches on the situation in Afghanistan, the peaceful revival and development of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan and, in general, the promotion of the economic integration in the regional and interstate level which is prime example and blessing of its neutrality status.
The UN Regional Centre on Preventive Diplomacy for Central Asia is to promote the dialogue between the Central Asian states with the aim to prevent potential threats, strengthen stability and durability of efficient interstate relations in the region. The neutrality and preventive diplomacy are the complementary mechanism that is actively used to find new constructive areas of international cooperation that meet the challenges of modernity. Turkmenistan having a neutrality status is trying its level best to minimize miseries and promote opportunities, to lessen conflicts and establish peaceful co-existence in the region and around the globe. The model of Turkmen neutrality is the phenomenon of the international diplomacy, given the fact that the country was declared the first neutral state in the modern history on December 12, 1995.
The international initiatives of the President of Turkmenistan has achieved many milestones in terms of socio-economic prosperity, reduction of poverty, availability of employment, regional connectivity and world partnerships. Its neutrality status was, and is, instrumental in the success of its foreign policy and internal security. All these are the principles of Turkmen neutrality, which has become an effective mechanism for protecting national interests and diversifying Turkmenistan’s international cooperation.
Neutrality of the Turkmenistan is considered today as the most important factor for ensuring sustainable development on a regional and global scale. The legal status of the neutrality of Turkmenistan was highly appreciated as an important tool for establishing interstate dialogue, an effective mechanism for developing relations of mutual understanding and good-neighborliness. It combines the firm principles of international law and diplomacy as well as constructive practice of peace-making dialog and realization of the preventive measures based on proposal and implementation of large-scale initiatives aimed at the consolidation of international partnership. Turkmenistan practically proves that the neutrality, peace-loving and good neighbourliness have been and remained to be the core of its foreign policy.
To conclude, the TAPI (Turkmenistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan and India) Gas Pipeline is an important factor of Turkmenistan’s Neutrality Doctrine which is based on peace, non-violence and peaceful resolution.




