“Soon shall We show them Our signs in the universe and in their own selves, until it becomes clear to them that this Qur’an is indeed the truth. Is it not enough that your Lord is a witness over everything?” (Qur’an;41:53); “We did not create heaven and earth and everything between them to no purpose. That is the opinion of those who disbelieve…” (Qur’an; 38: 27), “Verily in the heavens and the earth are Signs for those who believe. (Qur’an; 45:3). “To God belongs the Mystery of the heavens and the earth. And the Decision of the Hour (of Judgment) is as the twinkling of an eye, or even quicker: for God hath power over all things.” (Qur’an; 16:77).
Introduction
Religion is increasingly playing more part in human behaviour and their daily lives. A new Pew Research Center study of the ways religion influences the daily lives of Americans finds that people who are highly religious are more engaged with their extended families, more likely to volunteer, more involved in their communities and generally happier with the way things are going in their lives. Such trends are also noticed in other communities worldwide with varying degrees. The followers of three Abrahamic faiths believe that God created the universe and governs it as per His laid down rules. The atheists reject such a set of beliefs. In philosophy there are many rational, metaphysical, logical, empirical, or subjective arguments for the existence of God. Interestingly the conclusions reached by science recently were mentioned 1400 years ago in the last Testament; The Quran, which provides theological, philosophical and scientific evidence of existence of God.
The rapid progress in the scientific knowledge during last few centuries has opened new windows of knowledge thus giving new dimensions in understanding theology. Science is beginning to see the entire universe as an interlinked network of energy and information. Our capacity for fulfillment can come only through faith and feelings. But our capacity for survival must come from reason and knowledge. Anyone who endeavors to seek the way to God, with an open mind keeping aside the existing ideas can reach Him. This study is presented in two parts:
Part-1
• Introduction
• Principle of Conceptualization of Faith:
• Philosophical Arguments:
• Universe Models
• Quantum Entanglement
Part-2
(In next issue of DJ)
• Holographic Universe
• Religious Arguments
• Attributes of God & Science
• Proofs of God, Attributes
• God, Science & Universe
• Conclusion
While Part-1 is being presented here, Part-2 will be covered in the next issue of DJ.
PART-1
THE GOD AND UNIVERSE
A central, common core of Islam, Judaism and Christianity is the affirmation of the reality of One, and Only One, God. Adherents of Abrahamic faiths believe that there is a God who created the universe out of nothing and who has absolute sovereignty over all his creation, this includes, of course, human beings, who are dependent upon His creative power. Many realize the existence of God (theists) through their wisdom or the messages by prophets and men of wisdom, while others deny existence of any God or supreme power, known as atheists. The varieties of atheism are numerous, but all atheists reject such a set of beliefs. In philosophy there are three major, purely rational, arguments for the existence of God that have had a significant influence on the history of philosophy of religion. A wide variety of arguments exist which can be categorized as metaphysical, logical, empirical, or subjective. The existence of God is subject to lively debate in philosophy, the philosophy of religion being almost entirely devoted to the question and in popular culture. Certain theists acknowledge that belief in the existence of God may not be amenable to demonstration or refutation, but rests on faith alone. The atheistic conclusion is that the arguments and evidence both indicate there is insufficient reason to believe in the existence of God, and that personal subjective religious experiences are indistinguishable from misapprehension.
Principle of Conceptualization of Faith
Before discussing theological, philosophical and scientific arguments for existence of God, a fresh look at the principles of conceptualization of faith by renowned Arab scholar Sheikh Ali Tantawi is important:-
1) We have no doubts about anything that we can perceive through our senses we all accept this fundamental truth.
2) Certainty about past and present events received through a reliable source is as reliable as the certainty we would have had if we had been present.
3) The human imagination is unable to encompass things which are beyond the reach of human senses.
4) We have no right to refuse the existence of certain things which are not perceptible thorough senses.
5) The human mind, therefore, cannot go deeply into the realm of metaphysics. The human mind goes off balance when it tries to dominate the unlimited or infinite; it becomes the victim of impossible contradictions when it delves deeply into anything which is unlimited.
6) Faith in the existence of God is something which is inborn in every individual. It is a natural instinct and an urge – rather like the sexual drive. So we can say that man is an animal with a religion. This instinct may be overrun by physical desires, passion, ambition and craving for material comfort. However, when overcome by fear, danger or other crises, it rejects these desires and appears in its true and natural form.
7) The human language lacks a better expression, with a wider scope and range of meaning, which would include the spiritual aspects of love of God and His attributes, for which normal words do not express the actual meanings.
8) The human self is always eager to rise to sublime heights, to an unknown world, the identity of which can only be acquired. Man becomes convinced, intuitively rather than intellectually, that this material life is not the ultimate goal and that there is beyond doubt another world beyond this. This subjective and psychological perception and intellect are the proofs of the existence of another world called the Hereafter.
9) The Lord of this universe is fair and that anyone who is just will not allow for injustice. He will not let the oppressive person go unpunished, nor will he deny justice to anyone who has suffered unfairly in this world.
10) Belief in another world (Hereafter) is a natural consequence to the belief in the existence of God.
Philosophical Arguments
Philosophers and theists have come out with many popular arguments to support the existence of God (covered previously in DJ), being summarized here:
Cosmological Arguments
The cosmological argument was first introduced by Aristotle (384-322. B.C) and later refined in Western Europe by the celebrated Christian theologian, Thomas Aquinas (1225-1274.CE). It is known as: ‘The Basic First-Cause Argument’ and states: “Every event must have a cause, and each cause must in turn have its own cause, and so forth. Hence, there must either be an infinite regress of causes or there must be a starting point or first cause.” The conclusion thus follows that there must be an initial prime mover, a mover that could cause motion without any other mover; the God.

Teleological Arguments
Teleology is the use of ultimate ‘Purpose’ or ‘Design’ as a means of explaining natural phenomena. St. Paul, with many others in the Greco-Roman world, believed that the existence of God is evident from the appearances of nature: “Ever since the creation of the world his invisible nature, namely, his eternal power and deity, has been clearly perceived in the things that have been made” (Romans;1:20). The most popular, because the most accessible, of the theistic arguments is that which identifies evidences of design in nature, inferring from them a ‘Divine Designer’. The argument from design takes a story with acknowledged disclosure possibilities e.g. the interrelated parts of a clock and uses this as a catalyst to evoke a disclosure around some ever-broadening purpose patterns of the universe, in relation to which one can speak of God in terms, for example, of eternal purpose. William Paley (1805 C.E) in his ‘Natural Theology’ presented it with an analogy of a ‘clock’ found in a remote desert which existed not by pure chance, being a complex machine it has to be a product of an Intelligent Designer i.e. there must be a clockmaker. In the same way Paley argues that the universe is much more complex and manifestly designed. The extraordinary design is evident from planets and galaxies at the cosmic level to human cells and atoms at the quantum level. Therefore this world must have an Intelligent Creator. This form of the argument can be seen as an inference to the best explanation. That is given the remarkable phenomena of the universe, the best possible explanation for this, must be the existence of God. Paley next argues that if one accepts the above reasoning one is then obliged to accept the reasoning he gives for the universe as a whole. The world is intricate and well-designed for the purpose of supporting life it is the product of an ‘Intelligent Designer’. Else the world is the product of random physical processes.
Stephen Hawking, in his book; Brief History of Time” published in 1988, did not deny the existence of God in the creation of Universe but wrote that in order to understand the existence of the world, imagining of an unseen creator is compatible with the rules of science. This book was a best selling book in that year. However he changed his views in his latest book, though he does not rule out the possibility of God, which he thinks the ‘scientific rules’ can be called, but he denies the God as creator.
Richard Dawkins (hard core atheist) on Intelligent Design: Intelligent Design holds that certain features of the natural and living worlds show evidence of having been designed and are not the result of blind and purposeless forces as maintained by pure neo-Darwinism. No more, no less. It’s intriguing that Richard Dawkins seems to agree, even though he previously maintained that ‘biology is the study of complicated things that give the appearance of having been designed for a purpose’. According to him: ‘if you look at the details of biochemistry, molecular biology, you might find a signature of some sort of designer…and that designer could well be a higher intelligence from elsewhere in the universe’. In a nutshell, that’s Intelligent Design..
Ontological Arguments
Anselm’s Argument: The modern form of the ontological argument in modern western philosophy was made famous by St. Anselm (1033-1109 C.E) and Descartes (1596-1650). The argument rests on the premise that existence is a predicate that a being could have or lack. Anselm’s argument can be summarized as: “God is a being than which nothing greater can be conceived, a being than which nothing greater can be conceived to exist in our thought. Either a being than which nothing greater can be conceived exists in thought alone and not in reality or a being than which nothing greater can be conceived exists both in thought and in reality. If the greatest conceivable being existed in thought alone we could think of another being existing in both thought and reality. Existing in thought and reality is greater than existing in thought alone. Therefore: A being than which nothing greater can be conceived (God) exists in thought and in reality.”
Simply by pure reason, without any reference to the world, Anselm argues for God. A key feature of these kinds of arguments is that they try to show not only that God exists, but that he necessarily exists. That is, He cannot, not exist. The existence of God is an essential feature of its being just like the angles of a triangle always add up to 180 degrees. It would be impossible to think of God without it existing. Descartes [French mathematician, scientist, and philosopher, considered as the father of modern philosophy] writes: “From the fact that I cannot think of a mountain without a valley, it does not follow that a mountain and a valley exist anywhere, but simply that a mountain and a valley, whether they exist or not are mutually inseparable. But from the fact that I cannot think of God except as existing, it follows that existence is inseparable from God. Hence, the very essence of God, to even make the concept of God intelligible it must exist”.
Criticism
One of the major arguments proposed against the existence of God in contemporary western philosophy is the problem of evil. It is based upon the inability to reconcile the magnitude of evil in the world with the all-loving nature of God. John Hick describes the problem from the perspective of its proponent, “If God perfectly loves, God must wish to abolish all evil; and if God is all-powerful, God must be able to abolish all evil. But evil exists, therefore God cannot be both omnipotent and perfectly loving.” This thus causes difficulty for the Judeo-Christian-Islamic God who possesses both qualities of being all-loving and omnipotent. David Hume (1711-1776 C.E. the British philosopher and historian who argued that human knowledge arises only from sense experience) is a proponent of this view and argues that the sheer amount of evil, which may outweigh the good, in the world makes dubious that a deity exists.
The main response to this kind of an argument is known as the Free-Will Defense. It is based on the premise that for God to create self-directly and independent agents like humans, he had to grant a certain amount of freedom to them, and this freedom would inevitably result in human-to-human evil. It has been proposed that there need not be a contradiction between God creating morally free agents and making it the case that all their actions turn out to be good. But it can be argued that in that case, are the beings really as free as humans? If all our actions were predestined in this way, there would be a sense in which we would not be free and only an allusion be created thereof. Although God could have created beings of this sort, they would have amounted to mere puppets and not vibrant beings as envisioned by God.
Free Will Defence
The primary difficulty with the problem of evil is resolving the apparent conflict between the reality of evil in the world and the claim that God is Omniscient-All knowing, Omnipotent-All powerful and Wholly Good. One version of the free will defense is to compare the current state of the world with a world in which all actions were good and no evil was possible. It is important here to point out that the good that is being referred to is ‘moral good.’ That is, it is good that is a result of the conscious actions of people. This is distinct from ‘natural good’ or ‘natural evil’ which maybe result from non-human causes. The free will defense (FWD) theorist points out that in order for man to be in a position to do ‘moral good’ he must be ‘significantly free.’ That is, he must be in a position to make a choice between making a morally good or evil action. Given that in the current world (World-1) human agents are given this freedom, a certain level of moral evil is unavoidable. This world would still be more preferable to a possible World-2 in which there were no free actions (thus no freedom) but all actions performed were entirely good.
Critique
A critic of this defense will point out that if God is all-powerful (Omnipotent) then it ought to be in His capacity to create a World-3 in which humans had freedom, yet all their actions turned out to be good. Thus their actions would be predetermined to be good, yet they would still have the free option of choosing between morally good or bad actions. The agent would have the freedom to choose any action they like; it would just be that whatever choice they made it would turn out to be good. This would entirely be within God’s power since He is omnipotent and is only limited by logical impossibilities.
The challenge for the FWD theorist is to show that Freedom and Causal Determinism are both mutually inconsistent. It can’t both be the case that humans are free agents, and that their actions are causally predetermined. The crucial question is, can God can create any world? Alvin Plantinga attempts to answer this question. First, he points out that Leibniz was mistaken in thinking that God would have to, and thus did, create the best possible world. Plantinga argues that there can be no such thing as the best possible world, since to any world one more unit of pleasure or goodness can be added to make it even better. Thus it seems implausible to think of the best possible world as existing. This then is one instance when God cannot create any world.
Secondly, he argues that God cannot create a world in which Man is both significantly free, yet his actions are already determined. His proof on this premise has to do with a thought experiment. We can imagine a case in the present world in which we know given certain conditions a person would hypothetically engage in a morally evil action. It would not be impossible for God to create a world that were almost identical the present world, except that the person would then not engage in the evil. Since, to do so would deny him the freedom of individuality and his personality. That is, for God to ensure that he not engage in the evil would deny his freedom. The only other solution is for God to not create the world at all. He argues that for any world God could create, which included freedom, there is at least one action on which Man would go wrong, or else he could not create any world at all, this phenomenon he calls ‘Transworld Depravity’. Therefore, for God to create a world in which humans had moral freedom, the existence of both Good and Evil is necessary.
Free Will- Islamic Perspective
Basing on the basic doctrine of Islam, Muslims scholars have deduced a balanced view about free will. According to the great Spanish Muslim philosopher Averroës (Ibn Rushd); ‘The human actions depend partly on his own free will and partly on causes outside his control. Man is free to wish and to act in a particular manner, but his will is always restrained and determined by exterior causes. These causes spring from the general laws of nature; God alone knows their sequence.’
Some philosophers see the existence of Qualia (or the hard problem of consciousness) as strong arguments against materialism and therefore for the existence of material and immaterial entities. The Transcendental Argument suggests that logic, science, ethics, and other serious matters do not make sense in the absence of God, and that Atheistic Arguments must ultimately refute themselves if pressed with rigorous consistency. The atheists believe that existence of God cannot be proved through science. However the scholars have done a lot of research work to prove it scientifically, which forms basis for this paper. We start with the biggest creation, The Universe:
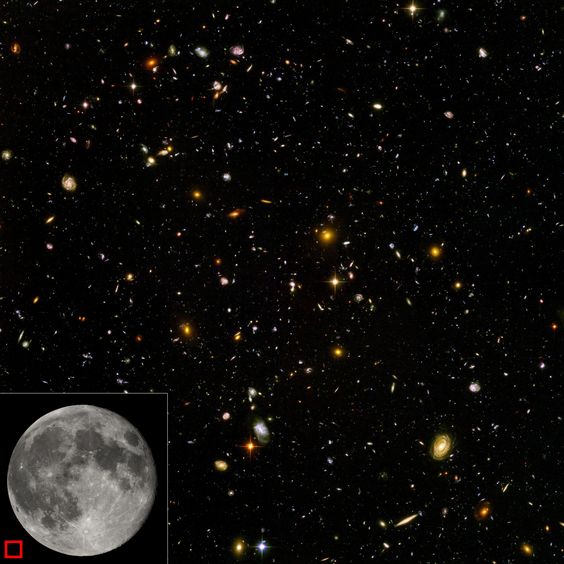

Universe Models
Universe: Sign of Creator
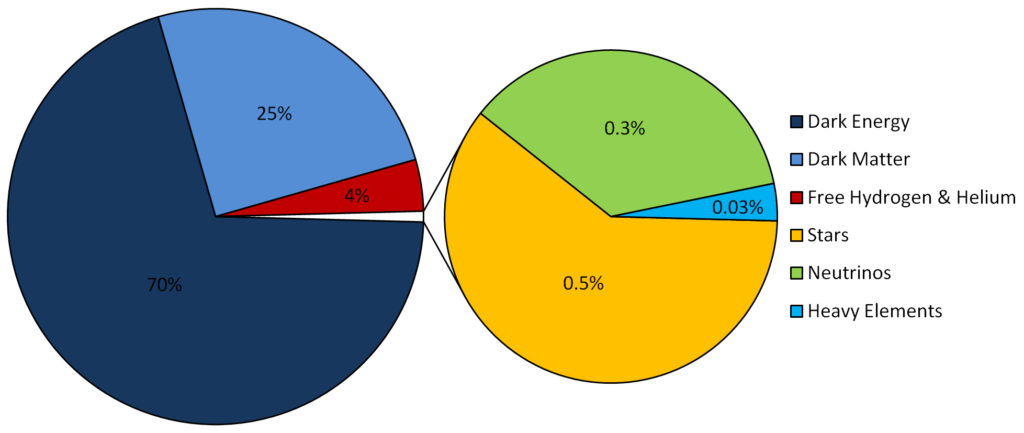
The universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists, including all matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. Definitions and usage vary and similar terms include the cosmos, the world and nature. Scientific observation of earlier stages in the development of the universe, which can be seen at great distances, suggests that the universe has been governed by the same physical laws and constants throughout most of its extent and history. There are various multiverse theories, in which physicists have suggested that our universe might be one among many universes that likewise exist.
The universe is immensely large and possibly infinite in volume. The region visible from Earth (the observable universe) is a sphere with a radius of about 46 billion light years, based on where the expansion of space has taken the most distant objects observed. For comparison, the diameter of a typical galaxy is only 30,000 light-years, and the typical distance between two neighbouring galaxies is only 3 million light-years. As an example, our Milky Way Galaxy is roughly 100,000 light years in diameter, and our nearest sister galaxy, the Andromeda Galaxy, is located roughly 2.5 million light years away. There are probably more than 100 billion galaxies [1011] in the observable universe. Typical galaxies range from dwarfs with as few as ten million [107] stars up to giants with one trillion [1012] stars, all orbiting the galaxy’s center of mass. A 2010 study by astronomers estimated that the observable universe contains 300 sextillion 3×1013 stars.
The part where the Universe is not just bigger than you can possibly comprehend, but according to recent evidence, billions of times larger than that. What It Says: That the universe is big, so big, that just that fact, just its mere bigness, is enough to blow your tiny ant mind. And it just keeps getting bigger. Let’s examine the famous Hubble Ultra Deep Field image, the most massive photo ever taken. It shows that there are approximately 10,000 galaxies. Each of those galaxies contains anywhere from ten million to one trillion stars. The average star is roughly a million times the size of Earth.
And yet, with all that junk, the Universe is more than 90 percent empty space. All of that, in this tiny photo. A photo that took 400 orbits and 800 exposures to take. And the kicker?
The photo covers one thirteen-millionth of the entire night sky. It leaves one alternately awash with spiritual wonder and horrified feelings of utter insignificance. Actually imagining just how infinitesimal you are in the scope of the universe is like autoerotic asphyxiation: it’s not as pleasant as you would think, and if you do it wrong you can end up a vegetable. You possibly imagine that much space and that many planets and stars and atoms smashing together without intelligent life forming? Now it’s just a matter of getting around that pesky general relativity and well be chilling with aliens in no time. Or, like, a million years.
So all that just said about how big the universe is (at least 90 billion light years)? That is small beans. The Cosmological Horizon is here to make your day a whole lot more complicated. Since we can only observe stellar bodies that have had some effects on us (usually bombarding us with light), there is an outer limit to what we can see of the universe. Hence, the observable universe. What about the rest? The parts of the universe beyond our StarCraft-style fog of war? Well, according to some math we have no interest in going into the size of the actual universe that is so large that if the universe we just described (the impossibly, mind-bogglingly large one) were the size of a quarter, the actual universe would be the size of the Earth.
Level of Mind Blowingly: The sound of one hand clapping for a tree falling in the woods while no one around except a guy whose skull is wired with C4 explosive. Hence the mere vastness of universe indicates the greatness of its Great Creator.
The Eternal Universe
Towards the end of the 19th century, atheists formulated a worldview that they thought explained everything; they denied that the universe was created saying that it had no beginning but had existed forever. They claimed that the universe had no purpose but that its order and balance were the result of chance; they believed that the question of how human beings and other living things came into being was answered by Darwinism. They believed that Marx or Durkheim had explained history and sociology, and that Freud had explained psychology on the basis of atheist assumptions.
However, these views were later invalidated in the 20th century by scientific, political and social developments. Many and various discoveries in the fields of astronomy, biology, psychology and social sciences have nullified the bases of all atheist suppositions. In his book, God: The Evidence, The Reconciliation of Faith and Reason in a Post secular World, the American scholar Patrick Glynn from the George Washington University writes:
The past two decades of research have overturned nearly all the important assumptions and predictions of an earlier generation of modern secular and atheist thinkers relating to the issue of God. Modern thinkers assumed that science would reveal the universe to be ever more random and mechanical; instead it has discovered unexpected new layers of intricate order that bespeak an almost unimaginably vast master design. Modern psychologists predicted that religion would be exposed as a neurosis and outgrown; instead, religious commitment has been shown empirically to be a vital component of basic mental health…
Few people seem to realize this, but by now it should be clear: Over the course of a century in the great debate between science and faith, the tables have completely turned. In the wake of Darwin, atheists and agnostics like Huxley and Russell could point to what appeared to be a solid body of testable theory purportedly showing life to be accidental and the universe radically contingent. Many scientists and intellectuals continue to cleave to this worldview. But they are increasingly pressed to almost absurd lengths to defend it. Today the concrete data point strongly in the direction of the God hypothesis. Science, which has been presented as the pillar of atheist, materialist philosophy, turns out to be the opposite. As another writer puts it, “The strict materialism that excludes all purpose, choice and spirituality from the world simply cannot account for the data pour in from labs and observatories.”
Assuming the validity of the old model of an ‘Eternal Universe’, Hugh David Politzer, an American theoretical physicist who shared the 2004 Nobel Prize in Physics, opposed the idea of a creation: The universe was not a created object, if it were, then it would have to be created instantaneously by God and brought into existence from nothing. To admit creation, one has to admit, in the first place, the existence of a moment when the universe did not exist, and that something came out of nothingness. This is something to which science cannot accede. By supporting the idea of an eternal universe against that of creation, Politzer thought that science was on his side. However, very soon, the fact that Politzer alluded to by his words, “if it is so, we must accept the existence of a creator”, that is, that the universe had a beginning, was proven.
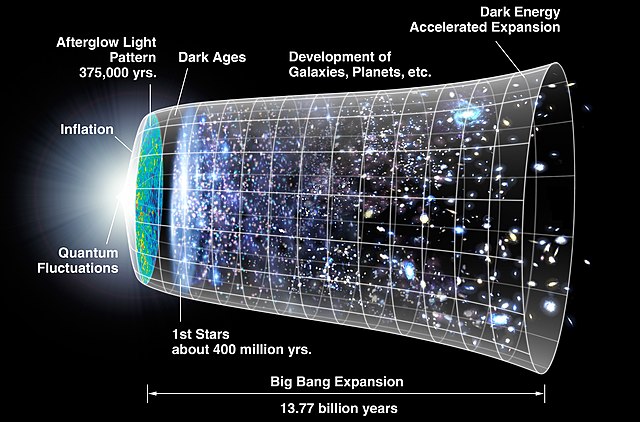
The Big Bang
This proof came as a result of the “Big Bang” theory, perhaps the most important concept of 20th century astronomy. The Big Bang theory was formulated after a series of discoveries. In 1929, the American astronomer, Edwin Hubble noticed that the galaxies of the universe were continually moving away from one another and that the universe was expanding. If the flow of time in an expanding universe were reversed, then it emerged that the whole universe must have come from a single point. Astronomers assessing the validity of Hubble’s discovery were faced with the fact that this single point was a “metaphysical” state of reality in which there was an infinite gravitational attraction with no mass. Matter and time came into being by the explosion of this mass-less point. In other words, the universe was created from nothing. In the face of proven scientific facts, atheists have been squeezed into a corner. Anthony Flew, an atheist professor of philosophy at the University of Reading and the author of Atheistic Humanism, makes this interesting confession:
Notoriously, confession is good for the soul. I will therefore begin by confessing that the Stratonician atheist has to be embarrassed by the contemporary cosmological consensus. For it seems that the cosmologists are providing a scientific proof of what St. Thomas contended could not be proved philosophically; namely, that the universe had a beginning. So long as the universe can be comfortably thought of as being not only without end but also without beginning, it remains easy to urge that its brute existence, and whatever are found to be its most fundamental features, should be accepted as the explanatory ultimate’s. Although I believe that it remains still correct, it certainly is neither easy nor comfortable to maintain this position in the face of the Big Bang story.
Some materialists have a relatively logical view of this matter. For example, the English materialist physicist, H.P. Lipson, unwillingly accepts the scientific fact of creation. He writes: I think …that we must…admit that the only acceptable explanation is creation. I know that this is anathema to physicists, as indeed it is to me, but we must not reject that we do not like if the experimental evidence supports it.
Thus, the fact arrived at finally by modern astronomy is this: time and matter were brought into being by an eternally powerful Creator independent of both of them. The eternal power that created the universe in which we live is God who is the possessor of infinite might, knowledge and wisdom.
Creation Models: Criticism & Analysis
It is patently obvious that the Big Bang means the creation of the universe out of nothing and this is surely evidence of willful creation. Regarding this fact, some materialist astronomers and physicists have tried to advance alternative explanations to oppose this reality. Mention has already been made of the Steady State Theory and it was pointed out it was clung to by those who were uncomfortable with the notion of “Creation From Nothingness” despite all the evidence to the contrary in an attempt to shore up their philosophy. There are also a number of models that have been advanced by materialists who accept the Big Bang theory but try to exorcise it of the notion of creation. One of these is the “oscillating” universe model; another is the “quantum model of universe”. Let us examine these theories and see why they are invalid.
Oscillating Universe Model
The oscillating universe model was advanced by the astronomers who disliked the idea the Big Bang was the beginning of the universe. In this model, it is claimed that the present expansion of the universe will eventually be reversed at some point and begin to contract. This contraction will cause everything to collapse into a single point that will then explode again, initiating a new round of expansion. This process, they say, is repeated infinitely in time. This model also holds that the universe has experienced this transformation an infinite number of times already and that it will continue to do so forever. In other words, the universe exists for eternity but it expands and collapses at different intervals with a huge explosion punctuating each cycle. The universe we live in is just one of those infinite universes going through the same cycle.
This is nothing but a feeble attempt to accommodate the fact of the Big Bang to notions about an infinite universe. The proposed scenario is unsupported by the results of scientific research over the last 15-20 years, which show that it is impossible for such an “oscillating” universe idea to come into being. Furthermore the laws of physics offer no reason why a contracting universe should explode again after collapsing into a single point: it ought to stay just as it is. Nor do they offer a reason why an expanding universe should ever begin to contract in the first place.
Even if we allow that there is some mechanism by which this cycle of contraction-explosion-expansion does take place, the crucial point is that this cycle cannot go on forever, as is claimed. Calculations for this model show that each universe will transfer an amount of entropy to its successor. In other words, the amount of useful energy available becomes less each time and every “opening” universe will open more slowly and have a larger diameter. This will cause a much smaller universe to form the next time around and so on, eventually petering out into nothing. Even if “open and close” universes can exist, they cannot endure for eternity. At some point it becomes necessary for “something” to be created from “nothing”. Put briefly, the “oscillating” universe model is a hopeless fantasy whose physical reality is impossible.
Quantum Model of Universe
The “Quantum Model of Universe” is another attempt to purge the Big Bang of its creationist implications. Supporters of this model base it on the observations of quantum (subatomic) physics. In quantum physics, it is to be observed that subatomic particles appear and disappear spontaneously in a vacuum. Interpreting this observation as “matter can originate at quantum level, this is a property pertaining to matter”, some physicists try to explain the origination of matter from non-existence during the creation of the universe as a “property pertaining to matter” and present it as a part of laws of nature. In this model, our universe is interpreted as a subatomic particle in a bigger one.
However this syllogism is definitely out of question and in any case cannot explain how the universe came into being. William Lane Craig, the author of The Big Bang: Theism and Atheism explains why:
A quantum mechanical vacuum spawning material particles is far from the ordinary idea of a “vacuum” (meaning nothing). Rather, a quantum vacuum is a sea of continually forming and dissolving particles, which borrow energy from the vacuum for their brief existence. This is not “nothing,” and hence, material particles do not come into being out of nothing.
So in quantum physics, matter “does not exist when it was not before”. What happens is that ambient energy suddenly becomes matter and just as suddenly disappears, becoming energy again. In short, there is no condition of “existence from nothingness” as is claimed. In physics, no less than in other branches of the sciences, there are atheist scientists who do not hesitate to disguise the truth by overlooking critical points and details in their attempt to support the materialist view and achieve their ends. For them, it is much more important to defend materialism and atheism than to reveal scientific facts and realities. In the face of the reality mentioned above, most scientists dismiss the quantum universe model. C. J. Isham explains that “this model is not accepted widely because of the inherent difficulties that it poses.” Even some of the originators of this idea, such as Brout and Spindel, have abandoned it.
A recent and much-publicized version of the quantum universe model was advanced by the physicist Stephen Hawking. In his book A Brief History of Time, Hawking states that the Big Bang doesn’t necessarily mean existence from nothingness. Instead of “no time” before the Big Bang, Hawking proposed the concept of “imaginary time”. According to Hawking, there was only a 10-43 second “imaginary” time interval before the Big Bang took place and “real” time was formed after that. Hawking’s hope was just to ignore the reality of “timelessness” before the Big Bang by means of this “imaginary” time. Stephen Hawking also tries to advance different explanations for the Big Bang other than Creation just as other Materialist scientists do by relying upon contradictions and false concepts. As a concept, “imaginary time” is tantamount to zero or non-existence like the imaginary number of people in a room or the imaginary number of cars on a road. Here Hawking is just playing with words. He claims that equations are right when they are related to an imaginary time but in fact this has no meaning. The mathematician Sir Herbert Dingle refers to the possibility of faking imaginary things as real in math as:
In the language of mathematics we can tell lies as well as truths, and within the scope of mathematics itself there is no possible way of telling one from the other. We can distinguish them only by experience or by reasoning outside the mathematics, applied to the possible relation between the mathematical solution and its physical correlate.
To put it briefly, a mathematically imaginary or theoretical solution need not have a true or a real consequence. Using a property exclusive to mathematics, Hawking produces hypotheses that are unrelated to reality. But what reason could he have for doing this? It’s easy to find the answer to that question in his own words. Hawking admits that he prefers alternative universe models to the Big Bang because the latter “hints at divine creation”, which such models are designed to oppose.
What all this shows is that alternative models to the Big Bang such as ‘Steady-State’, the ‘Open and Close Universe Model’, and ‘Quantum Universe Models’ in fact spring from the philosophical prejudices of materialists. Scientific discoveries have demonstrated the reality of the Big Bang and can even explain “existence from nothingness”. And this is very strong evidence that the universe is created by Allah, a point that materialists utterly reject.
An example of this opposition to the Big Bang is to be found in an essay by John Maddox, the editor of Nature (a materialist magazine) that appeared in 1989. In “Down with the Big Bang”, Maddox declares the Big Bang to be philosophically unacceptable because it helps theologists by providing them with strong support for their ideas. The author also predicted that the Big Bang would be disproved and that support for it would disappear within a decade. Maddox can only have been even more discomforted by the subsequent discoveries during the next ten years that have provided further evidence of the existence of the Big Bang. Some materialists do act with more common sense on this subject. The British Materialist H. P. Lipson accepts the truth of creation, albeit “unpleasantly”, when he says:
If living matter is not, then caused by the interplay of atoms, natural forces, and radiation, how has it come into being?…I think, however, that we must…admit that the only acceptable explanation is creation. I know that this is anathema to physicists, as indeed it is to me, but we must not reject that we do not like if the experimental evidence supports it.
The truth disclosed by science is this: Matter and time have been brought into being by an independent possessor of immense power, by a Creator. Allah, the Possessor of almighty power, knowledge and intelligence, has created the universe we live in.
Allah says: “And it is We Who have constructed the heaven with might, and verily, it is We Who are steadily expanding it”. (Qur’an, 51:47) “Do not the Unbelievers see that the heavens and the earth were joined together (as one unit of Creation) before We clove them asunder? (Big Bang) We made from water every living thing. Will they not then believe?” (Qur’an;21:30), “Moreover He Comprehended in His design the sky and it had been (as) smoke: He said to it and to the earth: “Come ye together willingly or unwillingly. “They said: “We do come (together) in willing obedience.” (Qur’an;41:11);“Who hath created and further given order and proportion” (Qur’an;87:2).
Random Universe
A second atheist dogma rendered invalid in the 20th century by discoveries in astronomy is the idea of a ‘Random Universe’. The view that the matter in the universe, the heavenly bodies and the laws that determine the relationships among them has no purpose but is the result of chance, has been dramatically discounted. For the first time since the 1970’s, scientists have begun to recognize the fact that the whole physical balance of the universe is adjusted delicately in favor of human life. With the advance of research, it has been discovered that the physical, chemical and biological laws of the universe, basic forces such as gravity and electromagnetism, the structure of atoms and elements are all ordered exactly as they have to be for human life. Western scientists have called this extraordinary design the “Anthropic Principle”. That is, every aspect of the universe is designed with a view that makes the existence of intelligent life inevitable.
Anthropic Principle
The basics of the “Anthropic Principle” may be summarized as follows:
The speed of the first expansion of the universe (the force of the Big Bang explosion) was exactly the velocity that it had to be. According to scientists’ calculations, if the expansion rate had differed from its actual value by more than one part in a billion billion, then the universe would either have recollapsed before it ever reached its present size or else have splattered in every direction in a way never to unite again. To put it another way, even at the first moment of the universe’s existence there was a fine calculation of the accuracy of a billion billionth. If the rate of expansion of universe would have been less or more than the size of a sand particle the universe would have not existed as is now.
The four physical forces in the universe (gravitational force, weak nuclear force, strong nuclear force, and electromagnetic force) are all at the necessary levels for an ordered universe to emerge and for life to exist. Even the tiniest variations in these forces (for example, one in 1039, or one in 1028; that is—crudely calculated—one in a billion billion billion billion), the universe would either be composed only of radiation or of no other element besides hydrogen.
There are many other delicate adjustments that make the earth ideal for human life: the size of the sun, its distance from the earth, the unique physical and chemical properties of water, the wavelength of the sun’s rays, the way that the earth’s atmosphere contains the gases necessary to allow respiration, or the Earth’s magnetic field being ideally suited to human life.
This delicate balance is one of the most striking discoveries of modern astrophysics. The well-known astronomer, Paul Davies, writes in the last paragraph of his book The Cosmic Blueprint, “The impression of Design is overwhelming”. In an article in the journal Nature, the astrophysicist W. Press writes, “There is a Grand Design in the Universe that favors the development of intelligent life.” The interesting thing about this is that the majority of the scientists that have made these discoveries were of the materialist point of view and came to this conclusion unwillingly. They did not undertake their scientific investigations hoping to find a proof for God’s existence. But most of them, if not all of them, despite their unwillingness, arrived at this conclusion as the only explanation for the extraordinary design of the universe.
In his book, The Symbiotic Universe the American astronomer, George Greenstein, acknowledges this fact: How could this possibly have come to pass [that the laws of physics conform themselves to life]? …As we survey all the evidence, the thought insistently arises that some supernatural agency or, rather Agency must be involved. Is it possible that suddenly, without intending to, we have stumbled upon scientific proof of the existence of a Supreme Being? Was it God who stepped in and so providentially crafted the cosmos for our benefit?
By beginning his question with “Is it possible”, Greenstein, an atheist, tries to ignore that plain fact that has confronted him. But many scientists who have approached the question without prejudice acknowledge that the universe has been created especially for human life. Materialism is now being viewed as an erroneous belief outside the realm of science. The American geneticist, Robert Griffiths, acknowledges this fact when he says, “If we need an atheist for a debate, I go to the philosophy department. The physics department isn’t much use.”
In his book Nature’s Destiny: How the Laws of Biology Reveal Purpose in the Universe, which examines how physical, chemical and biological laws are amazingly calculated in an “ideal” way with a view to the requirements of human life, the well-known molecular biologist, Michael Denton writes: The new picture that has emerged in twentieth-century astronomy presents a dramatic challenge to the presumption which has been prevalent within scientific circles during most of the past four centuries: that life is a peripheral and purely contingent phenomenon in the cosmic scheme.
In short, the idea of a ‘Random Universe’, perhaps atheism’s most basic pillar, has been proved invalid. Scientists now openly speak of the collapse of materialism. The supposition whose falsity God reveals in the Qur’an: “We did not create heaven and earth and everything between them to no purpose. That is the opinion of those who disbelieve…” (Qur’an; 38: 27) was shown to be invalid by science in the 1970’s.
One of the strangest properties of our universe is that it has very low entropy, meaning there is relatively low disorder, or conversely a large amount of order, among all of the particles. Think of it this way: Imagine a bomb full of sand exploding onto an empty surface—that’s the Big Bang. You would expect a pretty uniform heap of sand after the explosion, but instead, our universe immediately arranged into lots of sand castles seemingly for no reason and with no help, and we don’t really know why, Stefan Countryman, a physics Ph.D. student at Columbia University, explained to Gizmodo. The Big Bang could have (and maybe should have) resulted in a high-entropy mass of uniformly distributed, disorganized stuff. Instead, we’ve got star systems, galaxies, and galactic clusters all linked together with dark voids between them. We have order.
The “Intelligence Pervading the Universe” and the Collapse of Atheism
In the face of the scientific developments outlined, the acceptance of intelligent design by Anthony Flew, famous for defending atheism for many years, reflects a final scene in the process of collapse which atheism is being subjected to Modern science has revealed the existence of an “intelligence pervading the universe,” thus leaving atheism out of the equation.
In his book “The Hidden Face of God,” Gerald Schroeder, one of the creationist scientists who influenced Flew, writes:
A single consciousness, a universal wisdom, pervades the universe. The discoveries of science, those that search the quantum nature of subatomic matter, have moved us to the brink of a startling realization: all existence is the expression of this wisdom.
In the laboratories we experience it as information that first physically articulated as energy and then condensed into the form of matter. Every particle, every being, from atom to human, appears to represent a level of information, of wisdom.
Scientific research into both the functioning of the cell and the subatomic particles of matter has revealed this fact in an indisputable manner: Life and the universe were brought into being from nothing by the will of an entity possessed of a superior knowledge and wisdom. There is no doubt that the possessor of that knowledge and wisdom that designed the universe at all levels is Almighty God. God reveals these truths in Quran.
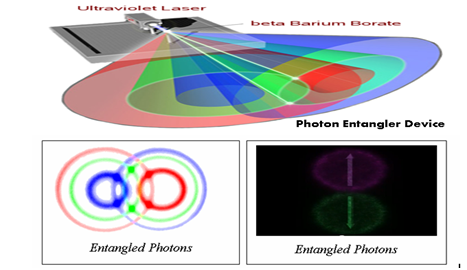
Quantum Entanglement
The God Effect!
Mysteries of Quantum Physics lead to God:
“To God belongs the Mystery of the heavens and the earth. And the Decision of the Hour (of Judgment) is as the twinkling of an eye, or even quicker: for God hath power over all things.” (Qur’an; 16:77).
If two electrons are created together, they are forever entangled, regardless of the distance between the two electrons; a change in quantum spin in one electron will immediately cause the other electron to change spin as well.
The part where you jiggle an electron on one side of the universe and an invisible force traverses millions of light years and smacks another electron into wiggling instantaneously, which is about a million years faster than is technically possible without time travel. In theory, you could separate two electrons by as much space as you wanted (say, the breadth of the universe), and they are still linked in such a way that actions taken on one would affect the other instantaneously. Meaning information is being transmitted at speeds faster than light. Meaning, if you want to really go nuts, time travel. And though the party pooping scientists have been busy coming up with limitations on the kind of information that could be transmitted, no one has yet been able to disprove the theory that there is an invisible force in the universe capable of affecting matter millions of light-years away instantly. So at Big Bang there was a point in the past in which every atom in the universe was condensed into a singularity. Which means everything is quantumly entangled. Some scientists have even gone so far as to claim that quantum entanglement shows that there is no such thing as space, and that everything in the universe is still touching.
Here is another explanation: When a photon (photon is a force carrier particle, usually polarized laser light) passes through matter, it will be absorbed by an electron. Eventually, and spontaneously, the electron will return to its ground state by emitting the photon. Certain crystal structures increase the likelihood that the photon will split into two photons, both of them with longer wavelengths than the original. Keep in mind that a longer wavelength means a lower frequency, and thus less energy. The total energy of the two photons must equal the energy of the photon originally fired from the laser (conservation of energy). When the original photon splits into two photons, the resulting photon pair is considered entangled.
The process of using certain crystals to split incoming photons into pairs of photons is called parametric down-conversion. Normally the photons exit the crystal such that one is aligned in a horizontally polarized light cone, the other aligned vertically. By adjusting the experiment, the horizontal and vertical light cones can be made to overlap. Even though the polarization of the individual photons is unknown, the nature of quantum mechanics predicts they differ. To illustrate, if an entangled photon meets a vertical polarizing filter, the photon may or may not pass through. If it does, then its entangled partner will not because the instant that the first photon’s polarization is known, the second photon’s polarization will be the exact opposite. It is this instant communication between the entangled photons to indicate each other’s polarization that lies at the heart of quantum entanglement. This is the “spooky action at a distance” that Einstein believed was theoretically implausible.
Quantum events obey the laws of quantum theory, which governs the behaviour of minute objects like atoms and subatomic particles, including photons of light. By contrast with the laws of ”classical” physics (which apply to the relatively large objects of the everyday world), quantum physics often exhibits behaviour that seems impossible. The connections that persist between distant but entangled particles are ”one of the deep mysteries of quantum mechanics. ‘These connections are a fact of nature proven by experiments, but to try to explain them philosophically is very difficult. Albert Einstein sneered at the very possibility of such a thing, calling it ”spooky action at a distance.” Scientists still (somewhat shamefacedly) speak of the ”magic” of ”quantum weirdness.” And yet all experiments in recent years have shown that Einstein was wrong and that action at a distance is real.
In the early 1930s, Einstein had problems with the whole of quantum physics, which is ironic given that it was partially based on his Nobel Prize winning paper on the photoelectric effect. What he didn’t like was the way quantum particles don’t have fixed values for their properties until they are observed. Why? Einstein couldn’t relate to a universe where probability ruled! That’s why he famously said that “Der Herrgott würfelt nicht!” or “The Lord doesn’t play dice!” Einstein believed that underneath these mathematical probabilities were fixed hidden realities that we just couldn’t see. That was why he, Podolsky and Rosen dreamed up the idea of what we now call “Quantum Entanglement” in 1935. It was to show that either quantum theory was incomplete, because it said there was no hidden information, or it was possible to instantly influence something at a distance. As that seemed incredible, he thought it showed that quantum theory was incorrect the way it had been presented with probabilistic mathematics. Quantum entanglement is at the heart of the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen (EPR) Paradox developed in 1935.
It did take a long time to prove that Quantum Entanglement truly existed. It wasn’t until the 1980s that it was clearly demonstrated. But it has been shown without doubt that this is the case. In 1982, at the university of Paris, a research team led by physicist Alain Aspect performed what may turn out to be one of the most important experiments of the 20th century. Aspect and his team discovered that: under certain circumstances subatomic particles such as electrons are able to instantaneously communicate with each other regardless of the distance separating them. The problem with this discovery is that it violates Einstein’s long-held tenet that no communication can travel faster than the speed of light.
In 1935 a famous paper by Albert Einstein, Boris Podolsky and Nathan Rosen challenged the quantum theory prediction that entangled particles could remain instantly in touch with each other. One of their objections was based on the speed limit imposed by Einstein’s Special Theory of Relativity: nothing can travel faster than the speed of light. Einstein and his colleagues preferred a more intuitive explanation of the simultaneous correlation between entangled particles, based on the idea that the match between them is ordained by their identical antecedents. The behaviour of each particle, they argued, is the product of hidden ”local” factors, not by spooky long-distance effects. But again and again in recent years, increasingly sensitive experiments have decisively proved that Einstein’s explanation was wrong and quantum theory is correct.
Since the 1970’s, physicists have been testing a prediction of quantum theory that ”entangled” particles continue to communicate with each other instantaneously even when very far apart. Entangled particles are identical entities that share common origins and properties, and remain in instantaneous touch with each other, no matter how wide the gap between them. Past experiments on entangled particles were carried out over distances of 100 yards or less. By showing that the link between two entangled particles survives even when they are seven miles apart, Dr. Gisin set a dramatic distance record.
The twin-photon experiment by Dr. Nicolas Gisin of the University of Geneva and his colleagues in June 1997 was the most spectacular demonstration yet of the mysterious long-range connections that exist between quanta events, connections created from nothing at all, which in theory can reach instantaneously from one end of the universe to the other.
In essence, Dr. Gisin sent pairs of photons in opposite directions to villages north and south of Geneva along optical fibers of the kind used to transmit telephone calls. Reaching the ends of these fibers, the two photons were forced to make random choices between alternative, equally possible pathways. Since there was no way for the photons to communicate with each other, ”classical” physics would predict that their independent choices would bear no relationship to each other. But when the paths of the two photons were properly adjusted and the results compared, the independent decisions by the paired photons always matched, even though there was no physical way for them to communicate with each other. In principle, it should make no difference whether the correlation between twin particles occurs when they are separated by a few meters or by the entire universe. This research is interesting not only from a scientific and philosophical point of view, but because of a very practical consequence: possible completely secure code could be created.

The Measurement or Observation
Effects on Behavior of Entangled Particles
One of the weird aspects of quantum mechanics is that something can simultaneously exist and not exist; if a particle is capable of moving along several different paths, or existing in several different states, the ‘Uncertainty Principle of Quantum Mechanics’ allows it to travel along all paths and exist in all possible states simultaneously. However, if the particle happens to be measured by some means, [observation or instrumental measurement] its path or state is no longer uncertain. The simple act of measurement instantly forces it into just one path or state. Physicists call this a ”collapse of the wave function.”
The amazing thing is that if just one particle in an entangled pair is measured, the wave function of both particles collapses into a definite state that is the same for both partners, even separated by great distances. The ‘double slit’ and ‘single slit’ experiments of electrons behaving as wave and particle respectively but once electron is observed it knows being observed and behaves as single shot electron not as wave. This is strange phenomena. The particle knows when it is being watched and when it was not. This shows the simple means of intelligence by reacting to visual stimuli. In the STI [Self thinking Interface] Device created by Physicist Roger R. Vogelsan in the early 70’ proved that there is ultimate knowledge in the FORCE which connects to all freed electrons. This FORCE knows everything its Omniscient.
Among several proposed explanations of all this is the ”many worlds” hypothesis: the notion that for every possible pathway or state open to a particle, there is a separate universe. For each of 10 possible pathways a quantum particle might follow, for example, there would exist a separate universe.
Since the 1970s Dr. John F. Clauser of the University of California at Berkeley, Dr. Alain Aspect at the Institute des Optics in Orsay, France, and others have been experimenting with pairs of entangled particles. One way to create a pair of entangled twins is to start with a single photon of ultraviolet radiation and pass it through a peculiar artificial mineral called a ”down-conversion crystal.” In the Swiss experiment, the crystal consisted of potassium niobate. The crystal splits the photon in two, producing two new photons that continue on in somewhat different directions, and whose combined energy equals the energy of their parent photon. The special quality of such pairs, as shown both by theory and experiment, is that they are entangled quantum mechanically. This means that if the polarization or energy or timing of one of the particles is measured, its indefinite state is destroyed and it falls into a definite state. The astonishing consequence of this is that the particle’s distant twin experiences exactly the same metamorphosis at the same moment, even though there is no physical link or signal between the two twins.
In Dr. Gisin’s experiment, as in earlier ones, no signal of any kind was transmitted between the photons, but despite this, one of the photons ”knew” what happened to its distant twin, and mimicked the twin’s response. This response took less than one ten-thousandth of the time a light beam would have needed to carry the news from one photon to the other at a speed of 186,282 miles per second. (In fact, the correlation between the two particles was presumably instantaneous. The Swiss experiment merely set an upper limit on the time required for the response as about three ten-billionths of a second.) Dr. Gisin’s experiment made use of a system of paired interferometers developed by Dr. James D. Franson of Johns Hopkins University, who is also a leading investigator of quantum effects.
”You start with an ultraviolet photon and split it into two photons. One goes one way and the other goes another way, both to identical interferometers. Entering its own interferometer, each photon must make a random decision as to whether it will travel a long pathway through the device or a short one. Then you look for a correlation between the pathways taken by the photons in their respective interferometers.” If the timing between the photons is exactly adjusted, each twin seems to know what the other is doing and matches its choice of pathway to coincide with that of its distant partner. Dr. Franson said of the correlation demonstrated over a seven-mile course by the Swiss experiment, ”It’s pretty amazing.”
Faster than Speed of Light
It is assumed that the numerical correlation between two particles different from information. Quantum theory is confirmed by experiments, and so is relativity theory, which prevents us from sending messages faster than light. It is unknown that there’s any intuitive explanation of what that means.
Tunneling
Another deep quantum mystery for which physicists have no answer has to do with ”tunneling” the bizarre ability of particles to sometimes penetrate impenetrable barriers. This effect is not only well demonstrated; it is the basis of tunnel diodes and similar devices vital to modern electronic systems. Tunnelling is based on the fact that quantum theory is statistical in nature and deals with probabilities rather than specific predictions; there is no way to know in advance when a single radioactive atom will decay, for example. The probabilistic nature of quantum events means that if a stream of particles encounters an obstacle, most of the particles will be stopped in their tracks but a few, conveyed by probability alone, will magically appear on the other side of the barrier. The process is called ”tunneling,” although the word in itself explains nothing. Dr. Chiao’s group at Berkeley, Dr. Aephraim M. Steinberg at the University of Toronto and others are investigating the strange properties of tunneling, which was one of the subjects explored by scientists attending the Nobel Symposium on quantum physics in Sweden. ”We find,” Dr. Chiao said, ”that a barrier placed in the path of a tunneling particle does not slow it down. In fact, we detect particles on the other side of the barrier that have made the trip in less time than it would take the particle to traverse an equal distance without a barrier — in other words, the tunnelling speed apparently greatly exceeds the speed of light. Moreover, if you increase the thickness of the barrier the tunneling speed increases, as high as you please. ”This is another great mystery of quantum mechanics.” Most physicists and engineers set aside the contemplation of quantum mysteries and are content to exploit the innumerable applications quantum physics has found in technology, including lasers, solid-state electronics and much more. But the sense of mystery has never been entirely suppressed.

The Cosmic Code
The late Rockefeller University physicist Heinz Pagels, like many other theorists, believed that quantum physics is a kind of code that interconnects everything in the universe, including the physical basis of life itself. In his book ”The Cosmic Code,” Dr. Pagels, an ardent mountain climber, wrote:
”I often dream about falling. Such dreams are commonplace to the ambitious or those who climb mountains. Lately I dreamed I was clutching at the face of a rock, but it would not hold. Gravel gave way. I grasped for a shrub, but it pulled loose, and in cold terror I fell into the abyss. Suddenly I realized that my fall was relative; there was no bottom and no end. A feeling of pleasure overcame me. I realized that what I embody, the principle of life, cannot be destroyed. It is written into the cosmic code, the order of the universe. As I continued to fall in the dark void, embraced by the vault of the heavens, I sang to the beauty of the stars and made my peace with the darkness.” Dr. Pagels was killed in a climbing accident in 1988.
Quantum Entanglement or the God Effect!
One of the main scientific goals of the world’s largest atom smasher, costing some 9 billion dollars, is to prove the existence of the Higgs boson (media call a God particle) which makes the universe possible by giving mass to everything including all of us and the objects we can touch! Quantum Entanglement (QE) or the God Effect is the working mechanism of the Higgs boson particle, because it’s so fundamental. Quantum Entanglement is at the heart of understanding how significant events across the universe operate at the macro- and micro- level in split-second synchronicity despite considerable distance between them. Quantum Entanglement suggests that information is exchanged faster between Quantum Entangled particles than the speed of light, which was deemed impossible per Einstein’s special theory of relativity proposed in 1905.
Quantum Entanglement: Applications
A ‘Type’ of “The God Connection”!
When God created the universe and the laws of physics, did He leave a ‘connection’ with all particles and forces within it? It seems there are themes and ‘designs’ in science that seem to repeat and recur in nature. Scientists and theologians have long wondered about the ‘dualism’ in particles and forces in the universe, nature, and morality. For example, matter and antimatter, positive and negative charges, male, female, good and evil, etc.
“And of everything We have created pairs that you may be mindful.” (Quran;51:49)
When atomic theory became the dominant theory of matter around the turn of the last century, the model of Neils Bohr, of hard round particles orbiting the atomic nucleus, was compared to the planetary system of our sun. The same theme is recurrent in galactic structure and the orbits of stars, star clusters, and gasses. It seemed that a basic structure was promulgated from the very smallest objects to the very largest.
We have since seen that the atom is much more complicated and that the objects orbiting the nucleus are not ‘hard’ and definite, but are both particle and wave in their structure. The nucleus itself is very complex and the once hard objects that we call neutrons, and protons are actually made up of ‘quarks’ and other nebulous subatomic particles.
In religion we have a belief that in order to communicate with God, a person enters into a state of consciousness that we call prayer. Through prayer, a spiritual connection is made to God and He hears our thoughts and we receive assurance that He acknowledges our wishes. Is there a similar “type” in the physical world for that connection? “It was We who created man and We know what dark suggestions his soul makes to him: for We are nearer to him than (his) jugular vein.” (Qur’an;50:16)
The idea in quantum entanglement is that every particle in a particle-antiparticle pair is in instant communication with the other particle, regardless of how far apart they are. It is a phenomenon that was experimentally proven, just recently, by scientists in Geneva Switzerland, in 2008. In this experiment a single particle – antiparticle pair was sent streaming away from the source in opposite directions, and they were detected when they were about 20 miles away from each other. The ‘entanglement’ phenomenon was proven when a ‘detection’ of one particle instantly produced an identical change in the other particle. This ‘instantaneous’ transmission of information defies Einstein’s theory of relativity and the speed of light. A calculation was made that determined that the speed of this experiment was at least 10,000 times the speed of light and perhaps was instantaneous.
The size of the particles of this discussion are at the subatomic level, far below ‘microscope’ level. Some scientists think that at this level, there is a universal ‘connection’ that transcends space/time and allows all particles to be ‘in contact’ with every other particle in the universe in a way that we have yet to understand. Below the ‘quantum’ or Planck level, the definitions of space and time become obscure and tend to blur. If all particles are somehow connected below the Planck level, it would seem to say that we all have a universal connection to each other and perhaps that is the medium through which prayer is channeled? That much is pure speculation, but if God created all the physical laws and the universe in such a way that He is never out of touch both spiritually and physically, and is omnipresent everywhere at once, it confirms what Christians, Jews & Muslims have always said about His presence and the ease with which we are in touch with Him. It means that He knows every thought, every event, and everything that happens in the universe. It also says that no matter how far you travel, or how much you transgress His will, He is always near.
Application in Highly Secure Communications
There are some real and amazing applications of Quantum Entanglement in our world. It can be used to produce unbreakable encryption. If we send each half of a set of entangled pairs to either end of a communications link, then the randomly generated but linked properties can be used as a key to encrypt information. If anyone intercepts the information it will break the entanglement, and the communication can be stopped before the eavesdropper picks up any data. Teleportation, Star Trek style is another aspect being explored.
Quantum Pseudo-Telepathy:
Telepathy is the transmission of information from one person to another without using any of our known sensory channels or physical interaction, it is experienced between individuals, love one’s at far off distances. The phenomenon of quantum pseudo-telepathy is mostly used as a powerful and explicit thought experiment of the non-local characteristics of quantum mechanics. Yet, the effect is real and subject to experimental verification, as demonstrated by the experimental confirmation of the violation of the Bell inequalities. The 2nd Caliph Omar bin Khatab (R.A) is reported to have communicated with the commander of the Islamic Army in battlefield hundreds of miles away. May be entanglement phenomena have something to explain!
Now in this age of quantum physics, the existence of anything can also be established by means of inferential argument, if direct argument or observation is not possible. It is established that inferential argument is valid with regard to the unseen micro, quantum world, it is also valid with regard to the existence of God. Bertrand Russell, although an atheist, in his book, “Why I am not a Christian”, has admitted this fact. He says that the argument centering on design, propounded by theologians to prove the existence of God, is scientifically valid. Since ancient days, theologians have argued that when there is a design there must also be a designer. As we see that our world is well designed, it compels us to believe that there is a designer – that is God.
Hence we find scientific explanation to the supernatural aspects unknown to man earlier, the mysteries of unknown (al-Ghaib) are being revealed with development in the field science. Allah says:
“Soon shall We show them Our signs in the universe and in their own selves, until it becomes clear to them that this Qur’an is indeed the truth. Is it not enough that your Lord is a witness over everything?” (Qur’an;41:53); “Verily in the heavens and the earth are Signs for those who believe. (Qur’an; 45:3). “To God belongs the Mystery of the heavens and the earth. And the Decision of the Hour (of Judgment) is as the twinkling of an eye, or even quicker: for God hath power over all things.” (Qur’an; 16:77).
To be continued ………
Next: The Science Leads to God-2
Reference/Links: http://justonegod.blogspot.com




