The Republic of Uzbekistan celebrates its “Constitution Day” on December 8 every year. It was adopted on December 8, 1992, by the 11th Session of the Supreme Council of the 12th convocation. It has already achieved elements of stability and sustainability in the spheres of economy, politics, civility and foreign policy. It unites its people. It minimizes differences among the different organ of the state. It upholds role of the law. It promotes politicization and democratization in the country.
The Preamble
“The people of Uzbekistan, solemnly declaring their adherence to human rights and principles of state sovereignty, being aware of their ultimate responsibility to the present and the future generations, affirming their commitment to the ideals of democracy and social justice, aspiring to a worthy life for the citizens of the republic, setting forth the task of creating a humane and democratic law-governed state adopt in the person of their plenipotentiary representatives the present Constitution of the Republic of Uzbekistan”.
A Complete Charter of Democracy
It is a complete charter of democracy. It is the custodian of human rights and last hope for the equality, tranquility and freedom of expression. It encourages societal transformation. It respects the will of people. It provides a solid foundation of building a new state and new society. Adoption of the constitution was the first giant step towards achieving socially oriented market economy. It developed a vibrant civil society in Uzbekistan. It protected the human interests, rights and freedoms.
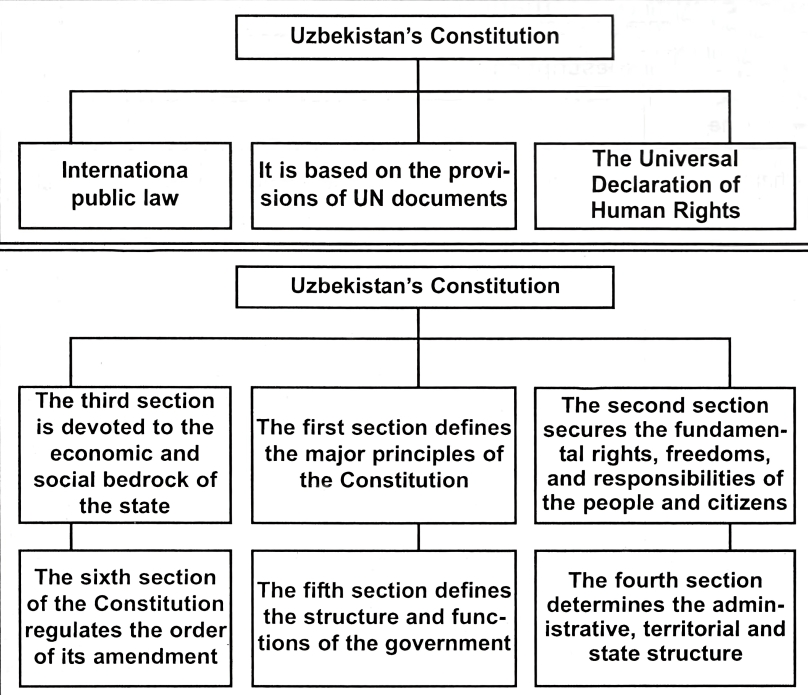
Uzbekistan’s Constitution consists of the preamble and six sections which include 26 chapters and 128 articles.
Total Sum of Political Intelligence
It is total sum of its political intelligence. It stands for fair play, equal rights and social justice. It guarantees basic civil rights and freedom. It encourages development of an independent press and association. It defends rights of the minorities. It is the basis for stable and sustained development of the country on the path of democratic development, the implementation of the principle ‘From a Strong State to a Strong Civil Society.
Leading Role in CIS
Now, Uzbekistan has the leading role in introducing and implementing different legal reforms in the CIS. Its constitution reflects the collective wisdom of its rulers and people alike. It promises the basic necessities of life. It assures free education, health and life. It is anti-discriminatory. It is people’s friendly. It is business and investment friendly. It guides all the organs of the state and strengthens democratic transition in the country. It portrays inspirations of its people. It guarantees the fulfillment of all the dreams of its people.
Forward Looking and Pragmatic
It is briefest and precise. It is forward looking and pragmatic. It regulates the most important public relations between citizens, society and the state. It establishes the foundations of the constitutional system, the principles of organization of state power. It is the foundation upon which rests the legal and political system, the system of the protection of the rights, freedoms and lawful interests of individuals.
Concept of Qualitative Life enacted
It guarantees qualitative life, and sustainable economic growth. It supports its diversified economy and steady democratic transition alike. Due to which, Uzbekistan’s economy has developed more than 3.5 percent and the GDP 2.5 times. Moreover, despite the ongoing global economic recession and financial crunch, Uzbekistan maintained GDP not less than 8.2 percent during 2008-2012. According to the Asian Development Bank (2015) during the last five ears the incomes of the country’s population have grown more than three-fold.
60 of the 128 articles of its constitution are empowered to the legal status of Uzbekistan’s people and citizens. It shows its people’s friendly orientation. It shows its love and respect of humanity.
Legal Foundation
It is crystal clear that the constitution has provided a legal foundation of building a democratic state. It establishes market economy and promotes a civil society in the country. Progressive constitution of Uzbekistan facilitated all the important organs the state to achieve the desired goals of socio-economic transformation, gradual economic liberalization and development of a vibrant civil society.
No Political or Administrative Deadlock
Its constitution assures political as well as economic stability. Constitutional provisions halt any political or administrative deadlock. It facilitates and removes all ambiguities.
Main Statutory Formation
| Parts | Description | Details/Articles |
| Part One | ||
| Chapter 1 | Fundamental Principles of State’s Sovereignty | Uzbekistan is a sovereign democratic republic. The state shall express the will of the people and serve their interests. It consists of sic articles. |
| Chapter 2 | Democracy | The people are the sole source of state power. All citizens of the Republic of Uzbekistan, regardless of their nationality, constitute the people of Uzbekistan. It has eight articles. |
| Chapter 3 | Supremacy of the constitution and the law | The Constitution and the laws of the Republic of Uzbekistan shall have absolute supremacy in the Republic of Uzbekistan. None of the provisions of the present Constitution shall be interpreted in a way detrimental to the rights and interests of the Republic of Uzbekistan. It has two articles. |
| Chapter 4 | Foreign Policy | The Republic of Uzbekistan shall have full rights in international relations. Its foreign policy shall be based on the principles of sovereign equality of the states, non-use of force or threat of its use, inviolability of frontiers, peaceful settlement of disputes, non-interference in the internal affairs of other states, and other universally recognized norms of international law. There is only one article to explain the importance and priorities of its foreign policy |
| Part Two | Basic Human and civil rights, freedoms and duties | |
| Chapter 5 | General Provisions | All citizens of the Republic of Uzbekistan shall have equal rights and freedoms, and shall be equal before the law, without distinction by sex, race, nationality, language, religion, social origin, convictions, individual and social status. It consists of three comprehensive articles. |
| Chapter 6 | Citizenship | In the Republic of Uzbekistan, uniform citizenship shall be established throughout its territory. Citizenship in the Republic of Uzbekistan shall be equal for all regardless of the grounds of its acquisition. Total articles are three. |
| Chapter 7 | Personal Rights and Freedoms | The right to exist is the inalienable right of every human being. Attempts on anyone’s life shall be regarded as the gravest crime. It contains 8 articles. |
| Chapter 8 | Political Rights | All citizens of the Republic of Uzbekistan shall have the right to participate in the management and administration of public and state affairs, both directly and through representation. They may exercise this right by way of self-government, referenda, and the democratic formation of state bodies. Articles 32-35. |
| Chapter 9 | Economic and Social Rights | Everyone shall have the right to own property. Everyone shall have the right to work, including the right to choose their occupation. Articles 36-42. |
| Chapter 10 | Guarantees of Human Rights And Freedoms | The state shall safeguard the rights and freedoms of citizens proclaimed by the Constitution and laws. Articles 43-46. |
| Chapter 11 | Duties of Citizens | All citizens shall perform the duties established by the Constitution. Articles.47-52 |
| Part Three | Society and the Individual | |
| Chapter 12 | The Economic Foundation of Society | The economy of Uzbekistan, evolving towards market relations, is based on various forms of ownership. The state shall guarantee freedom of economic activity, entrepreneurship and labor with due regard for the priority of consumer’s rights, as well as equality and legal protection of all forms of ownership. Articles. 53-55. |
| Chapter 13 | Public Associations | Trade unions, political parties, and scientific societies, as well as women’s, veterans and youth leagues, professional associations, mass movements and other organizations registered in accordance with the procedure prescribed by law, shall have the status of public associations in the Republic of Uzbekistan. Articles.56-62. |
| Chapter 14 | The Family | The family is the primary unit of society and shall have the right to state and societal protection. Articles.63-66. |
| Chapter 15 | The Mass Media | The mass media shall be free and act in accordance with the law. It shall bear responsibility for trustworthiness of information in a prescribed manner. |
| Part Four | Administrative and territorial structure and state system | |
| Chapter 16 | Administrative and territorial structure of the republic of Uzbekistan | The Republic of Uzbekistan shall consist of regions, districts, cities, towns, settlements, kishlaks and auls (villages) in Uzbekistan and the Republic of Karakalpakstan. Articles.68-69. |
| Chapter 17 | The Republic of Karakalpakstan | The sovereign Republic of Karakalpakstan is part of the Republic of Uzbekistan. Articles.70-75 |
| Part Five | Organization of State Authority | |
| Chapter 18 | Oliy Majlis of the Republic of Uzbekistan | The highest state representative body is the Oliy Majlis (the Supreme Assembly) of the Republic of Uzbekistan. It exercises legislative power. Articles.76-89 with lots of sub-clauses. |
| Chapter 19 | The President of the Republic of Uzbekistan | The President of the Republic of Uzbekistan is head of state and executive authority in the Republic of Uzbekistan. The President of the Republic of Uzbekistan simultaneously serves as Chairman of the Cabinet of Ministers. Articles.89-97. |
| Chapter 20 | The Cabinet of Ministers | The Cabinet of Ministers shall be formed by the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan and approved by the Oliy Majlis. |
| Chapter 21 | Fundamental Principles of Local Bodies of State Authority | The Soviets of People’s Deputies led by khokims are the representative bodies of authority in regions, districts, cities and towns, except in towns subordinate to district centers, and city districts. They shall act upon all matters within their authority, in accordance with the interests of the state and citizens. Articles.99-105. |
| Chapter 22 | Judicial Authority in the Republic of Uzbekistan | The judicial authority in the Republic of Uzbekistan shall function independently from the legislative and executive branches, political parties, and public organizations. Articles.106-116. |
| Chapter 23 | The Electoral System | All citizens of the Republic of Uzbekistan are guaranteed the equal right to vote. Every citizen shall have only one vote. Any citizen shall be eligible for election to public office. |
| Chapter 24 | The Procurator’s Office | The Procurator-General of the Republic of Uzbekistan and the procurator subordinate to him shall supervise the strict and uniform observance of the laws in the territory of the Republic of Uzbekistan. Articles. 118-121. |
| Chapter 25 | Finance And Crediting | The Republic of Uzbekistan shall have independent financial, monetary, and credit systems. Articles 122-124. |
| Chapter 26 | Defense and Security | The Armed Forces of the Republic of Uzbekistan shall be formed to defend the state sovereignty and territorial integrity of the Republic of Uzbekistan, as well as the peaceful life and security of its citizens. Articles 125-126. |
| Part Six | Procedure for Amending the Constitution | The Constitution of the Republic of Uzbekistan shall be amended by laws, passed by at least 2/3rds of the deputies of the Oliy Majlis of the Republic. |
Fundamental Principles and Strategic Priorities
In order to get rid of the burden and legacy of the totalitarian past, Uzbekistan adopted new constitution after its independence. Its various concepts defined the fundamental principles and strategic priorities of the state in the international arena and stands as a logical continuation of the strategy carried out by Uzbekistan since the first years of independence. Every sphere of life, political system, business sector and field of macro-economy along with guidance to foreign policy, diplomacy and the last but not the least defence policy has been pursued in the provisions of the constitution.
“Concept of further deepening democratic reforms, forming civil society and further development of market reforms and economic liberalization”
In November 2010 the honorable President Islam Karimov presented a concept of further deepening democratic reforms, forming civil society and further development of market reforms and economic liberalization. Earlier in 2005, the leadership of Uzbekistan initiated the first phase of democratic reform and as a first step the Referendum was held to approve the formation of bicameral parliament.
Constitution
| Different Organs | Details |
| Oliy Majlis (Parliament) | It consists of two Chambers: The Senate and The Legislative Chamber. The Legislative Chamber consists of 120 Deputies elected by territorial constituencies on multiparty basis. |
| Senate | It is the Upper Chamber of territorial representation and consists of 100 members (senators). The term of Senate’s office 5 years. |
| President | The president is the head of the state and executive power. The president of the Republic of Uzbekistan is simultaneously the Chairman of the Cabinet of Ministers of the Republic of Uzbekistan. He performs as a guarantor of democracy and observer of the constitution, represents Uzbekistan in international relations, concludes and ensures the observance of signed international treaties and agreements, forms and manages the cabinet of executive power, signs the laws, is the Supreme Commander-in-Chief, etc. |
| Cabinet of Ministers | It is formed by the president and approved by the Oliy Majlis of the republic. The Cabinet of Ministers is the supreme executive power of the state. The Cabinet of Ministers include the Prime Minister, First Deputy Prime Minister, Deputies of the Prime Minister, ministers, chairman of state committees, heads of large state concerns and corporations, and the Chairman of Karakalpakstan’s government. |
| Local Bodies of Power | The Councils of the People’s Deputies and Khokims (governors), elected by the councils, constitute the basis of the government in the regions, districts and towns. It is based on personal responsibility and meets the contemporary requirements for a strong government, which can resolve vital problems. |
| Judicial Authority | The court is the sole state body which administers justice. Judicial system of Uzbekistan consists of the following: The Constitutional Court which controls the execution of the Constitution and its principles by all the branches of the government; the Supreme Court of the Republic of Uzbekistan which is the paramount body in the system of civil, criminal and administrative legal proceedings; Supreme Economic Court is the ultimate judicial body in the sphere of regulating economic relations. |
The research analysis of the multi-party system in Uzbekistan shows that in the years of independence, it created a comprehensive legislative framework that provides the conditions for broad social and political activities of political parties. The legislative framework allows the factions of political parties more effectively represent the interests of their electorate, to participate actively in addressing major public issues.
Formation of new Society, Political System and Checks & Balances
President H.E. Islam Karimov introduced many short and long term reforms which are now paying the dividends. Reforms in the legislative branch, the separation of powers, human rights and the legal system and freedom of press and mass media are the few distinctive legal measures in the country. Nurturing NGOs and other societal institutions, furtherance of education on research and technology and the last but not the least administrative law are the salient features of its constitution.
Birth of Civil Society
Further deepening the democratic reforms and establishing the civil society in the country, adopted by the Parliament in November 2010, is a logical and naturally determined continuation of the process of democratic renewal and modernization launched since the early days of Uzbekistan’s independence. It gave birth to systematic and gradual democratic reforms in the country and created a vibrant civil society
Democratization of State Power and Governance
Democratization of state power and governance, the constitution amendments (articles 78, 80, 93, 96, 98)” of 2011 is now served as the most important document in the sphere of democratization of state power and governance. It ensured more balanced distribution of constitutional authorities among the President, the Head of state, legislative and executive branches of power. It was introduced the institute of vote of no confidence in the Prime Minister; the significant powers were delegated from the President to Senate – the Upper Chamber of the Parliament and the Cabinet of Ministers of the country; the authorities of local legislative councils were considerably expanded.
Establishment of Independent Electoral Process & Elections Commissioner
Systematic provisions/articles/amendments have already streamlined the duties and responsibilities, election procedure and other related items. “On elections to the Oliy Majlis of the Republic of Uzbekistan” and “On elections to the regional, district and municipal Kengashes of people’s deputies”, as well as the legislative acts on reforming and liberalization of the judicial system and expanding the sphere of application of Habeas corpus institute, implementation of the provisions of the Concept in the sphere of reforming the information system and ensuring freedom of speech, in particular, in the system of information and communication technologies and television, which play a decisive role in political modernization of the country.
Social participation, transparency, accountability
Social participation, transparency, accountability: “On normative-legal acts”, “On social partnership”, “On public control”, “On transparency of activity of bodies of state power and governance” and other legal acts will stimulate dynamic development of civil society, strengthening of its role in protecting constitutional rights and interests of people, transparency of activity of governing structures and informing the population about administrative decision making.
Private Ownership Guaranteed
“On protection of private ownership and guarantees of proprietors’ rights” secures the key principle of the priority of owners’ rights. Now all emerging contradictions and ambiguities in the legislation in terms of mutual relations between a proprietor and state bodies must be resolved in favor of the proprietor. “On family entrepreneurship”, “On competition”, “On guarantees of free entrepreneurship” and the decrees of the President adopted on their basis, namely “On measures to further improve business climate and provide more freedom to entrepreneurship” and “On measures to radically cut statistical, tax and financial reports, licensed types of activity and permissive procedures”, as well as other adopted decisions must become a guarantee for a sustainable development, diversification and modernization of the country’s economy and creation for this purpose of a favorable business climate and improvement of the attractiveness of the investment climate in the country.
Formation of a Liberalized and Democratic Society
It is the blessings of its progressive constitution that it has achieved a liberalized and democratic society which ensures sustainable and steady development of economy, qualitative life and a respectable place at the international arena. The comprehensive legal reforms succeeded to fulfill the requirements of a modern democratic state and vibrant society. The gamut of establishing the national statehood and political system based on the principles of checks and balances of separation of functions and power among legislative, executive and judicial branches of power, as well as providing priority of human interests, rights and freedoms is the essence of its constitution.
Paradigm Shift in Public Perceptions
Rightness of evolutionary phased and gradual advancement towards strategic objectives and tasks stipulated in the Constitution with due consideration of historical and national peculiarities and mentality to its people secured a grand victory which has provided an essential boost to its economy, politics, civility, populace and governance to work jointly for the betterment of its people at large with confidence, trust, respect and unity. Complexities of corporate world, modern ways of thinking, communication, interaction, privacy, political advancements and above all need for further democratic norms, judicial mechanism in the country, Uzbekistan may need to have a modern Constitution and perfect Strategy of achieving the objectives set in the Constitution. It requires a holistic approach along with a strong political commitment, patience, persistency and steadfastness.
Parliament Makes Vibrant
In order to further strengthening of the Parliament overall efficiency a number of amendments were introduced to the Main Law. The role of deputy associations and fractions of political parties was upgraded at all stages of scrutinizing and passing laws and normative acts. Now, not a single legislative act is passed without consideration of opinions and proposals of fractions i.e. deputy groups.
Meaningful judicial-Legal Reforms
Introduction of judicial-legal reforms has further strengthened the independence of courts as the most important component of establishing and democratizing society, ensuring rule of law, reliable protection of human rights and freedoms. Full abolishment of the supervisory functions of prosecutor bodies over judicial power has rectified many imperfections in the system. Now the prosecutor bodies no longer have a right to suspend the execution of court decisions. It expanded the use of the Habeas corpus institution to strengthen the judicial control in criminal process, improve the system and mechanisms of ensuring competition between defense and prosecution.
Criminal-Procedural Legislation
It criminal-procedural legislation has excluded the powers of court to instigate a criminal case and announce indictments on it. It has also enhanced the judicial control over investigation at the stage of pretrial proceedings. The application of such measures of procedural compulsion as removing from a post and placement of a person in medical institution has been relegated to courts. The adopted legislative acts provide the clear grounds to carry out the operational search activities. There are real legal guarantees of observing law, ensuring the human rights and freedoms and preventing administrative arbitrariness.
Concluding Remarks
Constitution of Uzbekistan is blessed with golden principles of checks and balances. It is anti-discrimination. It is anti-human. It is anti-development. It protects the basic human rights and necessities of life. It is people’s friendly. It is business and investment’s friendly. It is has forward looking orientation.
The Republic of Uzbekistan’s constitution is the best in the Central Asian Countries. It stabilized its macro-economy by initiating different meaningful laws. It protects investments and business activities. It saves the interests of local businessmen and entrepreneurs. It guarantees property and its proprietorship.
It discriminates intolerance and prejudice. It encourages women empowerment. It bans elements of hatred and unfair means in the society. It upholds true spirits of social justice. It institutionalizes traditions of rule of the law. It speaks about accountability, transparency and fair-play.
It spreads elements of politicization and democratization. It respects free will of people. The latest Presidential Election held in December 2014 highlighted concepts of free will/choice, equal opportunity and massive participation of the people and political parties alike.
Rise of NGOs and media outlets is the direct blessings of its constitution. NGOs act as watch-dog on different policies of the government. Mush-room growth of the mass media is another outcome of its enterprising constitution. NGOs stand for independence and impartial means for the evaluation of government policies and programs.
Labour class, factory workers and even seasonal farmers have been blessed and protected from any kind of exploitation in the country. There are certain provisions of the constitution which discourage child labour too. There is no scope and concept of child labour in the country as propagated by some Western Media. There is a system of salary & wage. There is judicial system to check the malpractice with workers etc. Thanks to its people’s friendly orientation of constitution.
It is a dignified document which cares about its people and their basic necessities of life. It provides path of glory and dignity. It is icon of national unity and sovereignty. It is custodian of human freedom and association. It provides guidelines of further strengthening of socio-economic prosperity, industrialization, renewable and above all social development.
It guides its foreign, defense and even financial policies to be implemented for the larger interests of its people. It establishes judicial system which cares about weaker factions and groups of the society. It safeguards the interests of minorities. It respects difference of faith, belief and religion. Religious tolerance is also the blessings of its constitution.




