China’s Communist Party (CPC) leaders in 18th Central Committee “Third Plenum” announced diversified revolutionary reforms titled “Decision on Major Issues Concerning Comprehensively Deepening Reforms”. It covers 16 areas and 60 individual items. It is the new China national character which creates new chapter in its socio-economic prosperity.
It reflects China’s national determination to remove all discriminations and works for greater economic integration, social cohesion, political motivation and a giant leap toward market economy. It also covers the human aspects of the throat-cut competition considering laborers, workers and common people an asset to sustainable economic development. It is the blue-print of blue economy. It chalks out policies and means to achieve greater industrialization, investment, taxes and revenues. It is above all the manifestation of people’s welfare.
President Xi Jinping and Premier Li Keqiang, announced several effective policy measures in social policy, mainly to unify rural and urban social security systems and to abolish controversial labor camps. The setting up of the National Security Committee and the Central Leading Group on Reform” indicates that the new leaders have a strategic vision to achieve the desired goals in the days to come.
It consists of major economic reforms to provide equal playing field to local and foreigner businessmen. It upholds the importance of foreign investment and announces new incentives/reforms for the local and international investors in China. It intends to overhaul the economic and financial sectors. It speaks highly about the importance of social development. It is all about welfare of the common people. It guarantees the environment and nature. It stands for corporate social responsibility, transparency, accountability and rule of the law. It pinpoints the hurdles in the further strengthening of social security in the country. It is a systematic approach to establish corporate governance and generation of revenues to get rid of debts. The last but not the least, it is the engine of further socio-economic development, attracting foreign investment, resolution of labour shortages/disputes and tax reforms. It has national, regional and global socio-economic ramifications which would be witnessed in the markets of the United Arab Emirates, Bangkok, Brussels, Washington, London and Frankford in the days to come. One of the major economic multiplier effects would be tremendous increase in the bilateral trade volumes between China-GCC/UAE, China-EU, China-Pakistan and of course China-US.
Broadly speaking according to newly announced reforms, the Chinese leadership will streamline its efforts among the local, central and private sectors/organ of the state to further develop interior and border cities Through a coordinated effort the level of investment in those regions will be enhanced, while authorities will guide efforts to upgrade technology in industrial and agricultural production according to each province’s comparative advantage. So, scientific management of governance will be followed to achieve desired goals in the days to come.
More focus will be given to service sector and transportation infrastructure, logistic entities and the international connectivity of hinterland cities in such regions will be enhanced through cooperation between the Chinese administrative authorities and incentivized private investors, both Chinese and foreign. Nurturing of trade activities will be increased in order to achieve sustainable development; ports and economic cooperation zones, therefore will also be opened to tourism and logistical investment in the country.

Third Plenum also pinpoints the importance of market economy claiming that market access will be further developed for all investors, including foreigners. To maintain the high standards of transparency, accountability and fair-play comprehensive measures will be institutionalized and predictability of official procedures will be taken swiftly. The experiment of transforming Shanghai into “a mainland Hong Kong” through the inauguration of the “pilot free trade zone” in the city was referred to as a breakthrough in the opening-up process. Moreover, gradually more such free trade zones will be established in different parts of the country. Through these zones, China will encourage local and national entrepreneurs to further invest overseas and loosen its grip on custom controls and financial inspections.
Further modernization of service sector stands tall in the Third Plenum. More attention will be given to health, finance, education, culture, e-commerce, elderly care, and child care and local and central government initiatives will be initiated in order to draw more international investment and increase domestic consumption. Other priorities were environmental protection, investment protection, and the consolidation of FTAs especially in the country’s close neighborhood.
The newly announced reforms talk about “scientific macro-regulation” and underlined it as a main function of the government in the opening-up process ahead. Efficient business management and coordinated regulation by central and local authorities will be put forth as keys to increasing productive efficiency. It also aims to mitigate structural risks by encouraging domestic demand and gradually re-organizing production to cater to domestic needs. On its part, the government will introduce new regulations to give more authority to private enterprises to take investment decisions, except in sectors concerning eco-safety, national security, energy and other underground resources, and the most vital public interests.
Environment protection is one of the most salient features of the Chinese reforms. From to-day to onward, new higher standards will be implemented on all firms (public & private) and investors will be held responsible regarding environmental protection, energy preservation, safety regulations, and technological inputs.
There will be overhauling in the system of GDP overall production-oriented appraisal and conferral of local governments’ and public administrators including factory managers and other public servants who bear a role in production. Performance will be rectified strictly in line with the emerging necessities of implementing higher standards regarding environmental protection, energy preservation, safety regulations and high-tech capital intensity in order to avoid unsustainable and self-destructive growth. Furthermore, a national platform will be formed to collect and streamline all data regarding housing and credit facilities. The risks associated with the combination of speculation, corruption, and financial complexity will be minimized.
Salient Features
(a) Interest Rate Liberalization and RMB’s full Convertibility
It is wide-ranging systematic mechanism consisting of improved market-based exchange rate formation mechanisms for the RMB, and speeding up RMB capital account convertibility by promoting the two-way opening of capital market, easing restrictions for cross-border capital and financial transactions, and establishing foreign debt and capital flow management systems. It has multiplier effects for the foreign investors, businessmen, and joint ventures.
Better currency exchange management would open new avenue of regional and international banking and finance cooperation speeding up of industrial production chains. China recently finalized its accords of currency swap including Pakistan and United Arab Emirates and hopefully, with better exchange rate scenarios, the volumes of bilateral trade, trade & commerce, investments (FDI & FPI), joint ventures, business activities, banking & finance and the last but not the least, insurance industries would be further flourished in the days to come.
It would accelerate interest rate liberalization by establishing a treasury bond yield curve that reflects market supply and demand. Building a deposit insurance system would be game changer in order to resource mobilization in the country.
It is hoped that a wide range of the financial reforms would be supportive for the further baking and financial development in the country. The deeper more sophisticated financial markets should make China better prepared for financial opening up, while financial opening up, especially RMB capital account convertibility, should attract experienced foreign institutions investors and expertise, speeding up the development of the onshore financial market.
| Different SOEs | Dividend payout ratios % |
| Tobacco companies | 20 |
| Resources | 15 |
| Ordinary companies | 10 |
| Military technology companies | 5 |
(b) State-Owned Enterprise (SOE) Reforms
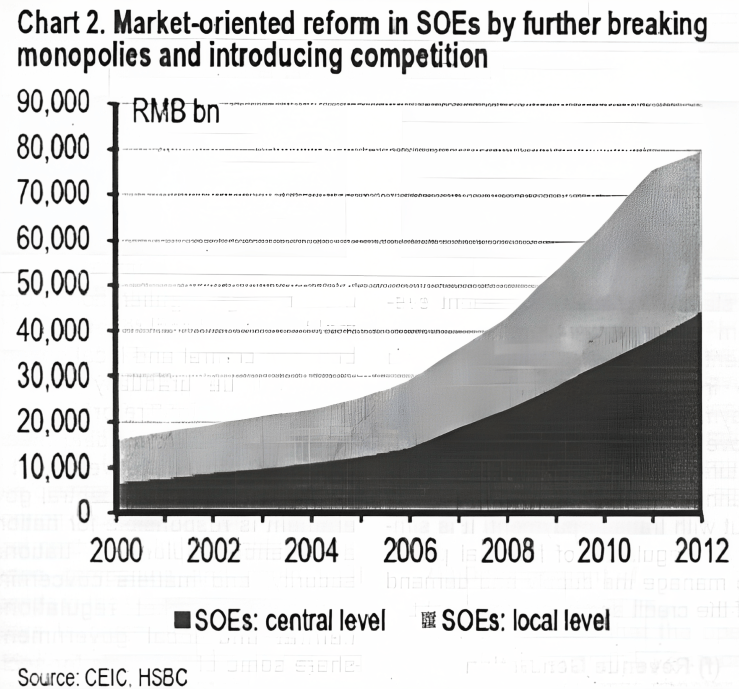
Generally, the lack of competition in the state owned sector has resulted in inefficiency, corruption and overcapacity. It emphasizes the importance of reducing government intervention in the economy, pledging to confine the administration to maintaining macro-economic stability, risk control and providing public goods and services. It would further strengthen of regulation and the provision of public services as well as introducing competition in the area of government tenders for services.
Pushing forward state-owned enterprise (SOE) reforms by forcing them to pay more dividends into the government’s social security fund pool would be beneficial for the country. Moreover, increasing the dividend payout ratio to 30 percent from current upper limit of 20 percent would strengthen government spending on social security.
The plan consists of integrated ownership of state-owned capital, collective capital and private capital, helping improve competitiveness of state capital. The reforms tell the improvement in the state-owned asset-management system, focusing on capital management. It facilitates the restructuring of selected SOEs into state-owned investment companies. Moreover, state capital investment should focus on key sectors related to national security, national economic lifeline industries, public services, science and technology, and ecological environment protection. To give fair chance to private sector and broadening of investments private investment is allowed to take part in state investment projects.
(c) Establishing of Modern Enterprise System and Improvement of Corporate Governance
Keeping in view the importance of free market economy and upholding of corporate governance it is pinpointed that all forms of administrative monopolies will be abolished while increasing the state’s contribution to public services. For natural monopoly industries run by state capital, a franchise operation and government supervision mechanism will be implemented. It is hope that it would create a healthy competition between the public & private entities in China and also encourage the potential foreign investors and businessmen to do business in China. It would also streamline the supply-demand chain in the domestic markets which would prove effective curbing the inflationary trends.
(d) Market Liberalization Reforms
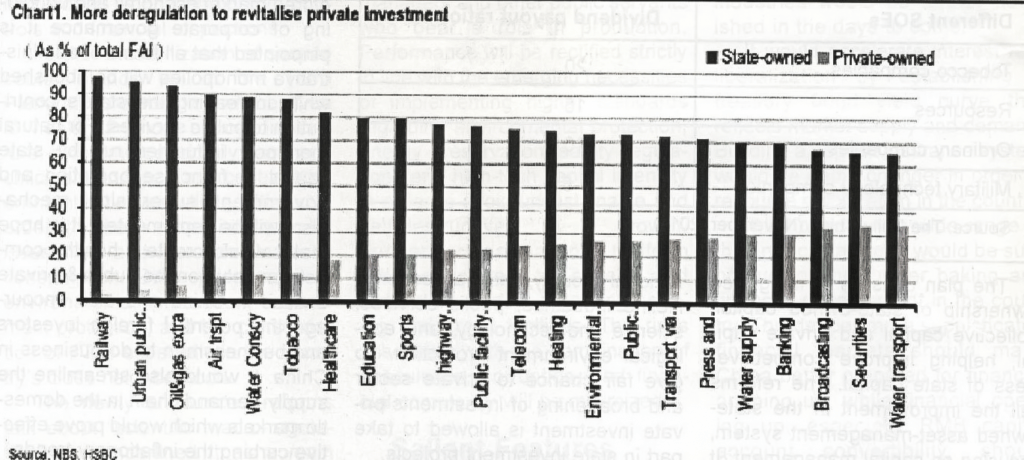
For the first time, the private and public sectors will be given equal rights. The first step would be establishing a fair, open and transparent market rules. Deregulation is needed to establish a unified mechanism for market entry so there is a level playing field. China wants to give foreign investors the same rights as local companies both before and after they set up business (aka a pre-establishment national treatment). Moreover, registration procedures will be further simplified. At the same time, regulators will clamp down on regional favouritism, unreasonable regulation, hidden barriers and monopolies.
It is hoped that the private companies, especially those in the services sector will be benefited most from deregulation and easier market access. Further, deregulation in banking, railway, telecom and culture sectors are expected to speed up.
The reforms has made crystal clear that any price that can be affected by the market must be left to the market and prices set by government will be confined to public utilities, public service and areas that are naturally monopolized. China will also push ahead with price reforms of water, oil and natural gas, electricity, transportation and telecommunication.
(e) Fiscal Reforms
The document of the Chinese reforms tells that a more transparent and standardized budget system is needed. It will help to shift the focus the size of the fiscal deficit to expenditure and policy, to establish a standard debt management system for central and local governments and a risk-alert system, and to improve government transfer payments. In principle, if a central government policy requires expenditure by a local government that cannot afford it, the center will help out with transfer payment. It is simply deregulation of financial power to manage the supply and demand of the credit and handling of debt.
(f) Revenue Generation
To streamline the local government’s revenue generation to optimal level, the fiscal revenue divide between central and local government will be gradually adjusted through taxation reforms. It is indeed a capacity building measure for all the local government in China. Moreover, the central government is responsible for national defence, diplomacy, national security, and matters concerning nationwide market regulations; central and local governments share some of the costs for social security and key regional construction project; local governments are mainly responsible for local public services.
(g) Improved Tax System
The reforms document includes broadening the local government tax base, simplifying the level of VAT, and adjusting the coverage and rate of the consumption tax, especially for energy intensive/big polluters and some high-end products. In addition to this the personal income tax system will be improved and property-tax legislation will be speeded up, as will resources tax reforms. The current environmental-protection fee will become an environment tax.
(h) Greater Scope of Private Sector
Permission has been given to qualified private capital to set up financial institutions such as small and medium sized (SME) banks, under enhanced supervision. It would be huge market booster for the country which gives attracts the foreign countries to open their financial centers including banks, insurance companies and could float bonds in the Chinese markets in the days to come. It is hoped that it would be beneficial for its banking and financial industry at large.
(i) Development of Capital market
Developing a multi-layered capital market, promoting a registration based stock issuing system and increasing the share of direct financing by developing the bond market and encouraging financial innovation are mentioned in the newly announced Chinese reforms. It would further strengthen the overall efficacy of the capital market in the country.

(j) Investments
It will no longer be necessary to apply for government approval for specific investments unless the projects are related to issues such as national security, ecological safety, manufacturing capacity and strategic resources exploration. Moreover, enterprises and individuals will be encouraged to invest overseas and undertake engineering and labour service cooperation projects at their own risk, through greenfield investment, M&A, equities and joint investment.
(k) Development of Free Trade Zones
It is announced that the opening of the Shanghai FTZ is only the beginning of new chapter in the Chinese trade and investment policy. The establishment of more free-trade zones would facilitate the joint ventures, value-addition and supportive world trade system and enhance bilateral, multilateral and regional cooperation. Reforms will be carried out in terms of market access, customs supervision and inspection and quarantine management.
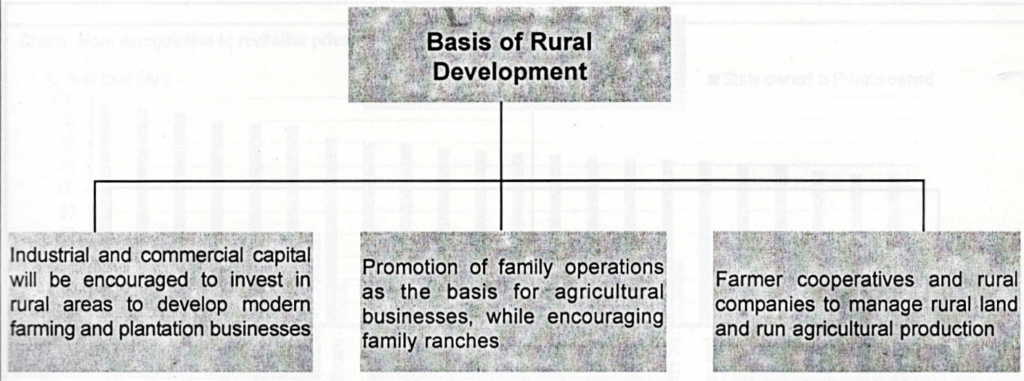
(l) Land reforms
According to the newly announced reforms land reforms would create a unified rural-urban construction land market to benefit farmers. Farmers will be given more property rights, in addition to establishing a more equitable and sustainable social security system and to provide basic but equal public services to all. China has started to clarify farmers’ rights to their contracted land and promised to finish registration and certification within five years, so that a legal foundation can be laid and the property rights of farmers safeguarded.
The CPC stressed that both public and non-public ownership are key components of China’s socialist market economy and vowed to protect the property rights of both. It reiterated that China will maintain the dominant role of public ownership economy and continue to develop the leading role of the state-owned economy.

It recognises that property rights of the public ownership economy and non-public ownership economy are equally inviolable. By protecting the property rights and legitimate interests of all kinds of ownership and ensuring that various ownerships have equal access to production factors, open and fair market competition and the same legal protection and supervision, potential and ingenious of nonpublic ownership economy could be boosted.
Granting the non-public ownership economy equal legal status with the public ownership economy will help build a foundation for the future expansion of the private sector, which in our view will be the driving force behind China’s long-term sustainable development.
(m) Improvement in Labour System
The new reform has abolished the 56 year old re-education through labour System as part of efforts to improve human rights protection. Mobility of the labour force has been made easy and effective.
(n) Patronized Urbanization
China values the contribution of its rural population in its onward socio-economic march. To reduce the widening development gap between rural and urban areas now farmers will be allowed to have equal access to the benefits of China’s development.
According to the newly announced Chinese reforms farmers will be given full property rights to their contracted land and they will be allowed to become shareholders in agriculture-enterprises by using their land-rights. It would further encourage the framers to produce more in the country. It would be an effective tool to eradicate the ratios of poverty, unemployment and above all curb the food shortage in some parts of the country.
Moreover, farmers are encouraged to transform their collectively owned property rights into a shareholding system. They can sell their share or use them as collateral or warranty. The share can be inherited. Meanwhile, the current homestead system in rural areas will be improved, and a pilot programme will be carried out to enable the mortgaging and transfer of farmers’ homesteads. A rural property-rights trading market will be established. It covers all aspects of the rural life, chain of production, economy and tradition so, it is a complete package.
(o) Improving the legislative and judicial system
It is pledged that people’s congresses should provide more supervision of the government’s financial budget and state-owned assets. Governments at all levels must report to the local people’s congresses before adopting important policies. Meanwhile, the independence and fairness of courts implies that the judicial system can be freed from local government interference. It is a necessary for ensuring that the market plays a larger role while reducing government intervention in private businesses.
(p) Easing the one-child policy
China’s one-child policy has been relaxed now. Family-planning policies have been applied throughout China since the 1970s in order to control the population growth. However, such policies were always loosely applied in the rural provinces and they were gradually relaxed
(q) Modern Cultural System
It is promised to develop a modern cultural system by stressing socialist values, in a bid to boost the country’s cultural influence. China is proud of its ancient culture, contribution towards civility, infrastructure, governance, arts, and above all human development.
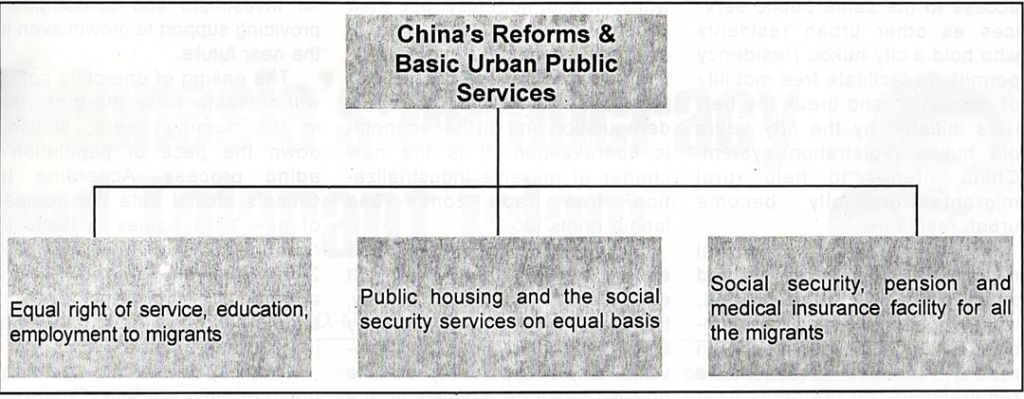
(r) Equalisation of basic services provisions
A total of 260 million migrant workers live in major cities within the country but do not have access to the same public services as other urban residents who hold a city hukou (residency permit). To facilitate free mobility of population and break the barriers initiated by the fifty years old hukou registration system, China intends to help rural migrants gradually become urban residents.
All restrictions on rural migrants settling in towns and small cities will be abolished, while those governing medium-sized cities will be loosened in an orderly manner. Reasonable requirements for settlement in large cities will be adopted, and strict control of population size in mega cities will institutionalized. It would promote sense of equality, freedom, healthy competition and above all production system in the country.
(s) Social security reforms
The leadership of China promises to establish a fairer and more sustainable social welfare system. The detail is given the following table as:
| Different Systematic Measures/Incentives | Elaboration |
| Nationwide pooling of a basic pension | Chinese leadership thinks that it is a basic human right which may bring desired goals of greater welfare for the workers in the public & private sectors. |
| Gradual suspending the retirement age of employees | It would be giant step for work security, productivity and efficacy in the corporate, service and industrial sectors. |
| Development the commercial insurance | China is sitting on the apex of industrial world. It would provide insurance cover to all the finished commodities services. |
| Speed up the reform of pension programmes for employees in public institutions affiliated with government | It encourages the employees to work at their best for the overall betterment of the country. |
| Urban and rural basic pension and basic medi-care insurance schemes | It would reduce the development gap between urban and rural areas and sense of privileged would be no more |
| Unified welfare system for all the Chinese citizen living in different parts | It would build a national character of equality, fair-play and excel. |
| Diversification of investments for national social security system, improve public housing security and supply system | Introduction of diversified investments options would be good for the country, institutions, corporation and insurance companies in the longer run |
(t) Ecological Reforms
Ecological reforms focus on building a beautiful China through improvements in the use of land and resources and ecological and environmental protection. It indeed China’s love, respect and care towards environment, nature, earth and global common heritage.
(u) Political Reforms
Political reform to advance socialist democracy based on unity of three elements the leadership by the Communist Party, the people being masters of their own country and administering the country in accordance with the law. In this regard, the reform of the CPC would be achieved raising the level of governance, to be scientific, democratic and according to the law.
Concluding Remarks
President Xi Jinping and Premier Li Keqiang announced a new socio-economic contract which would hopefully put their country on the right path of political glory, economic sustainability, financial stability and human dignity. It is the new beginning of deregulation and further economic liberalization. It is the new charter of massive industrialization, free trade zones and labour rights too.
It is the science of interest rate and currency management. It enhances the spirits of honesty, transparency, accountability among the employees and provides ample opportunity for the private sector to flourish in the reigns of state-owned enterprises. It facilitates the provisions of investments, and doing business across the country. It opens the gates of foreign banks and financial institutions to operate in the country of Confucius and avail win-win situation.
It values the importance of social security system in the country and strategies have already been announced to make it more productive, effective and supportive for all the citizens. Above all it is the systematic advancement of its social economy in the age of globalization 3.0 where interest is the ultimate weapon in the hands of free market economy’s handlers and resultant is the frequent political chaos, alarming ratios of poverty, unemployment, hunger, disease and underprivileged people living in the different parts of the world.
Some reform measures, such as curbing overcapacity and controlling local government spending, will involve short-term pain. But hopefully with strong political commitment, that specific matter will be resolved. Creating of a level-play field for private companies/entities and many other related reforms can unleash private sector demand for investment and consumption, providing support to growth even in the near future.
The easing of one-child policy will modestly raise the birth rate in the coming years, slowing down the pace of population’s aging process. According to China’s official data the number of new born babies is likely to rebound to the level of year 2000, implying around 1-1.5m addition from current level. It should have a meaningful impact in 2030 and beyond.
It is hoped that the combination of fiscal and financial reforms would boost productivity growth. Systematic urbanization would hold up infrastructure investment growth, and unleash the private investment power through easier access to funding for private companies. Deregulation would support for innovation. On the other hand, SOE reforms and urbanisation reforms would definitely boost efficiency in business.
The service sectors, allowing private companies to participate in railway, culture, financial services and healthcare would be giant leap in the future. The related supply of services will grow to match domestic and international demand. Moreover, the urbanisation reforms would assist shift labour from productivity farming work to higher productivity urban jobs, which itself is a substantial and sustainable productivity gain.
Historically, unlike previous third plenums, which mainly focused on economic issues, this time Chinese leadership has pledged to deepen diversified reforms, with the general goal of developing socialism with Chinese characteristics, and advancing modernization in the State governance system and governance capability.




